Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
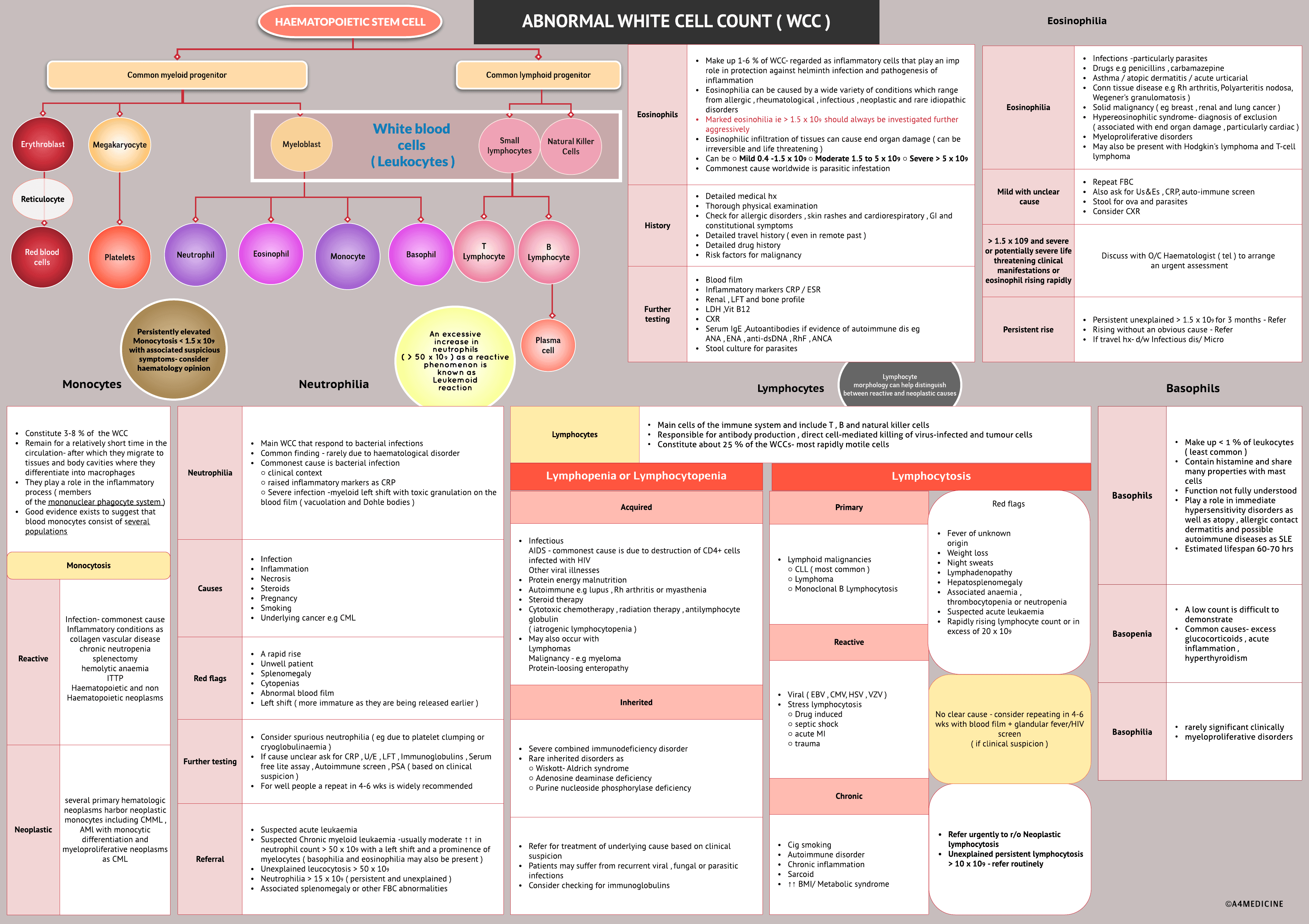
White cell count abnormalities -assessment and evaluation
Monocytes- Constitute 3-8 % of the WCC Remain for a relatively short time in the circulation- after which they migrate to tissues and body cavities where they differentiate into macrophages They play a role in the inflammatory process ( membersof the mononuclear phagocyte system ) Good evidence exists to suggest that blood monocytes consist of several populations
Monocytosis -Associated with infection and inflammatory process Causes can be○ Reactive monoytesInfection- commonest causeInflammatory conditions as collagen vascular diseasechronic neutropeniasplenectomyhemolytic anaemiaITTPHaematopoetic and non Haemtopoetic neoplasms○ Neoplastic Monocytesseveral primary hematologic neoplasms harbor neoplastic monocytes including CMML , AMl with monocytic differentiation and myeloproloferative neoplasms as CML
Neutrophilia-Main WCC that respond to bacterial infections Common finding - rarely due to haematological diorder Commonest cause is bacterial infection○ clinical context○ raised inflammatory markers as CRP○ Severe infection -myeloid left shift with toxic granulation on the blood film ( vacuolation and Dohle bodies )
causes-Infection Inflammation Necrosis Steroids Pregnancy Smoking Underlying cancer e.g CML. Red flags -A rapid rise Unwell patient Splenomegaly Cytopenias Abnormal blood film Left shift ( more immature as they are being released earlier ).Consider spurious neutrophilia ( eg due to platelet clumping or cryoglobulinaemia ) If...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.