Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
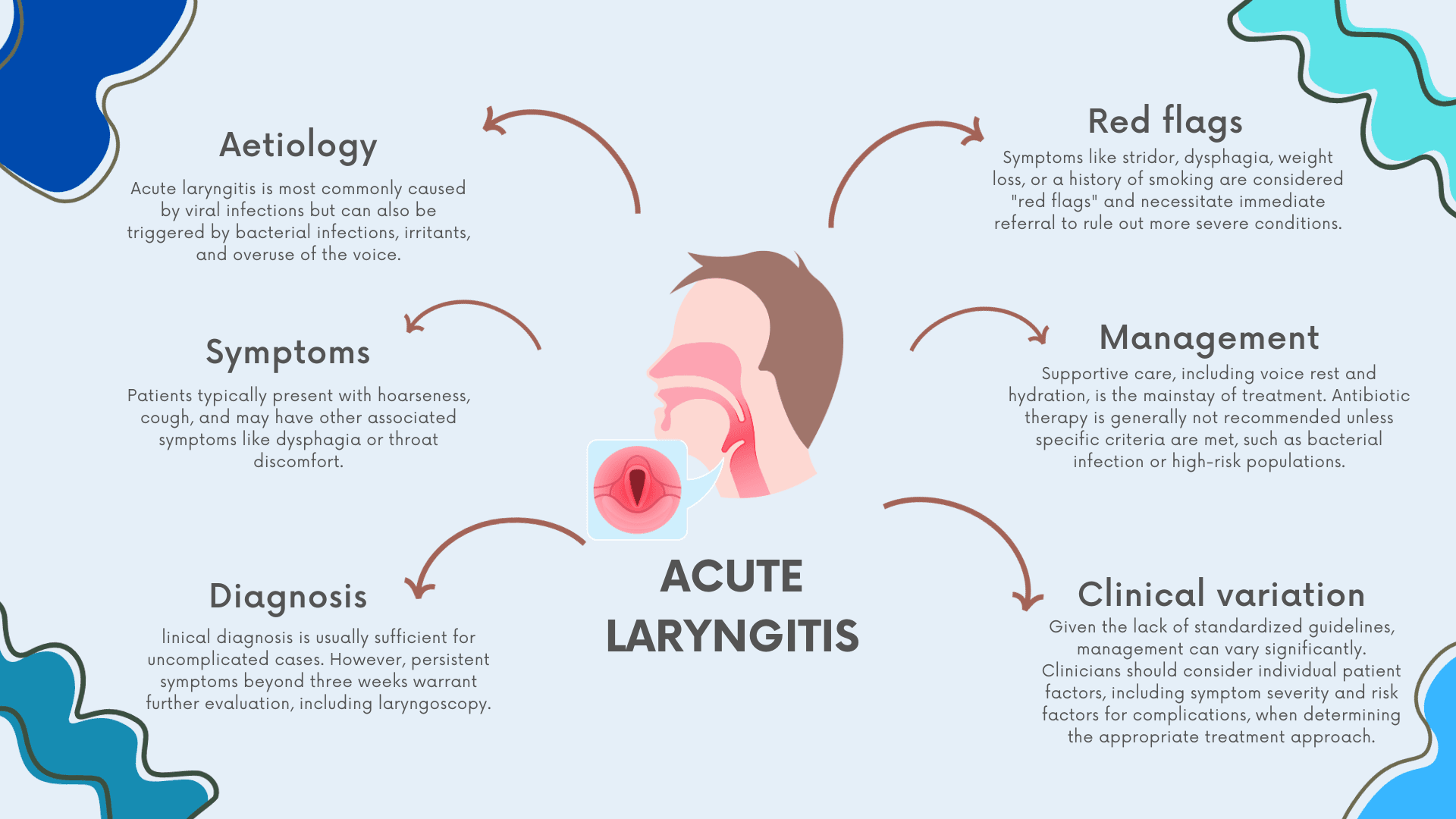
Acute laryngitis is a prevalent condition often seen in primary care, characterized by inflammation of the larynx that leads to symptoms like hoarseness, cough, and occasionally dysphagia. While most cases are self-limiting and caused by viral infections, the clinical presentation can vary and may sometimes signify more severe underlying conditions, including malignancies. Due to a lack of standardized guidelines, the diagnosis and management of acute laryngitis can be challenging for clinicians. This table aims to summarize the essential aspects of managing acute laryngitis, collating evidence-based recommendations and tips that can assist primary care clinicians in providing optimal care for their patients.
| Section | Subsection | Details | Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition & Impact | Definition | Inflammation of the larynx, affecting vocal cords. | Can be acute or chronic, infective or inflammatory, isolated or part of systemic disease.[1] | [1] |
| Impact on Health | Impacts physical health, quality of life, psychological wellbeing, and occupation if symptoms persist. | Common symptoms include hoarseness, impacting quality of life.[1] | [1] | |
| Etiology & Clinical Presentation | Viral Causes | Rhinovirus, adenovirus, influenza, parainfluenza, herpes species, HIV, coxsackievirus. | Most common cause of acute laryngitis. Often associated with upper respiratory tract infection.[10] | [10] |
| Bacterial Causes | HiB, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, β haemolytic streptococci, Moraxella catarrhalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae. | May... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.