Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
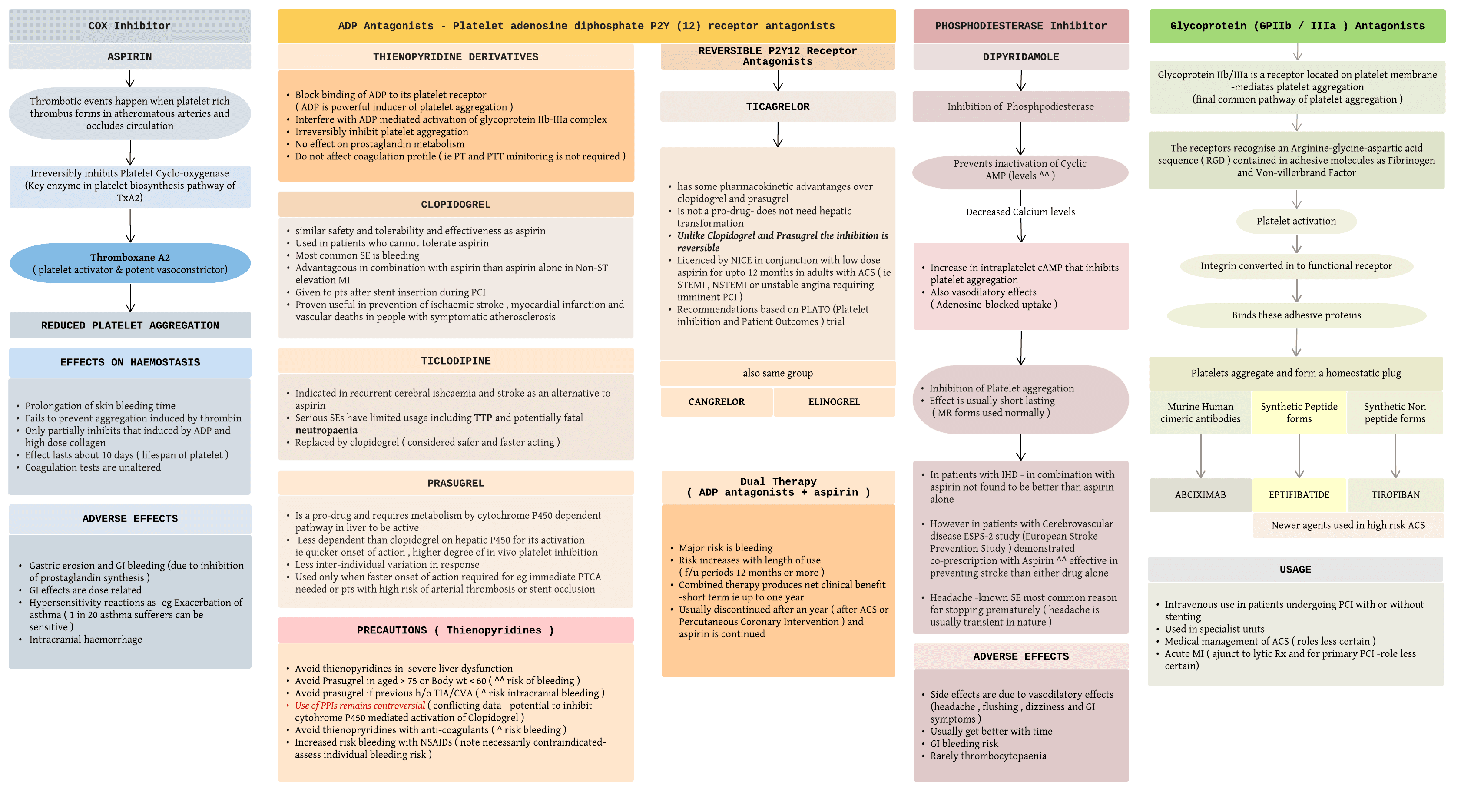
A visual summary of antiplatelet agents.
COX inhibitors Aspirin-Thrombotic events happen when platelet rich thrombus forms in atheromatous arteries and occludes circulation.Irreversibly inhibits Platelet Cyclo-oxygenase (Key enzyme in platelet biosynthesis pathway of TxA2).Thromboxane A2 ( platelet activator & potent vasoconstrictor).Prolongation of skin bleeding time Fails to prevent aggregation induced by thrombin Only partially inhibits that induced by ADP and high dose collagen Effect lasts about 10 days ( lifespan of platelet ) Coagulation tests are unaltered. Adverse effects-Gastric erosion and GI bleeding (due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis ) GI effects are dose related Hypersensitivity reactions as -eg Exacerbation of asthma ( 1 in 20 asthma sufferers can be sensitive ) Intracranial haemorrhage
ADP Antagonists - Platelet adenosine diphosphate P2Y (12) receptor antagonists
THIENOPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES Block binding of ADP to its platelet receptor ( ADP is powerful inducer of platelet aggregation ) Interfere with ADP mediated activation of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex Irreversibly inhibit platelet aggregation No effect on prostaglandin metabolism Do not affect coagulation profile ( ie PT and PTT minitoring is not required )
Clopidogrel-similar safety and tolerability and effectiveness as aspirin Used in patients who cannot tolerate aspirin Most common SE is bleeding Advantageous in combination with aspirin...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.