Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
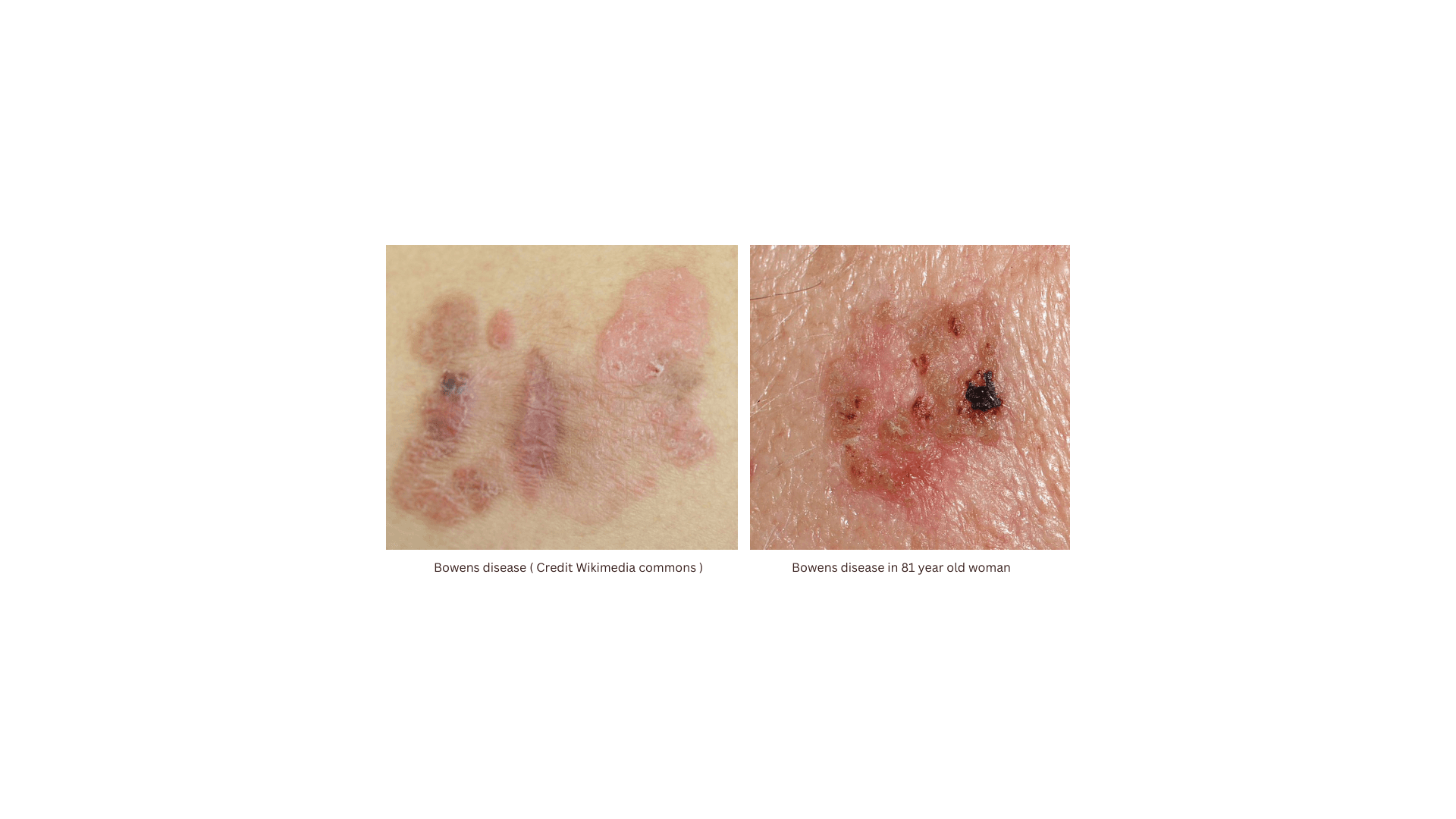
Bowen's disease is a premalignant skin condition that may progress to squamous cell carcinoma. It is characterized by slow-growing, well-demarcated erythematous patches or plaques, often found on sun-exposed areas of the skin. Treatment options include cryotherapy, Efudix® cream, and photodynamic therapy, with no clear evidence of one treatment being superior. Management requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving dermatologists, oncosurgeons, and plastic surgeons, depending on the presentation and various patient factors.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Bowen's disease (BD) is an in-situ squamous cell carcinoma of the epidermis, considered a precursor to overt squamous cell carcinoma. |
| Aetiology | Multifactorial, with higher incidence among Caucasians. Risk factors include UV radiation, carcinogens (e.g., arsenic), immunosuppression (e.g., post-organ transplantation), viral factors (HPV), and chronic injury or dermatoses. |
| Clinical Presentation | - Typically slow-growing erythematous patch or plaque. - Well-demarcated with scaling, crusting, or pigmentation. - Commonly on lower limbs and head/neck. - Can occur in various locations, often solitary, but up to 20% may have multiple lesions. |
| Progression Risk | About 3-5% of extragenital lesions and around 10% for genital lesions may progress to invasive carcinoma ( malignant potential ) |
| Incidence | Common in the Caucasian population, with an incidence of 1.42 per 1000 in some populations. |
| Dermoscopic Features | - White-yellow... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.