Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
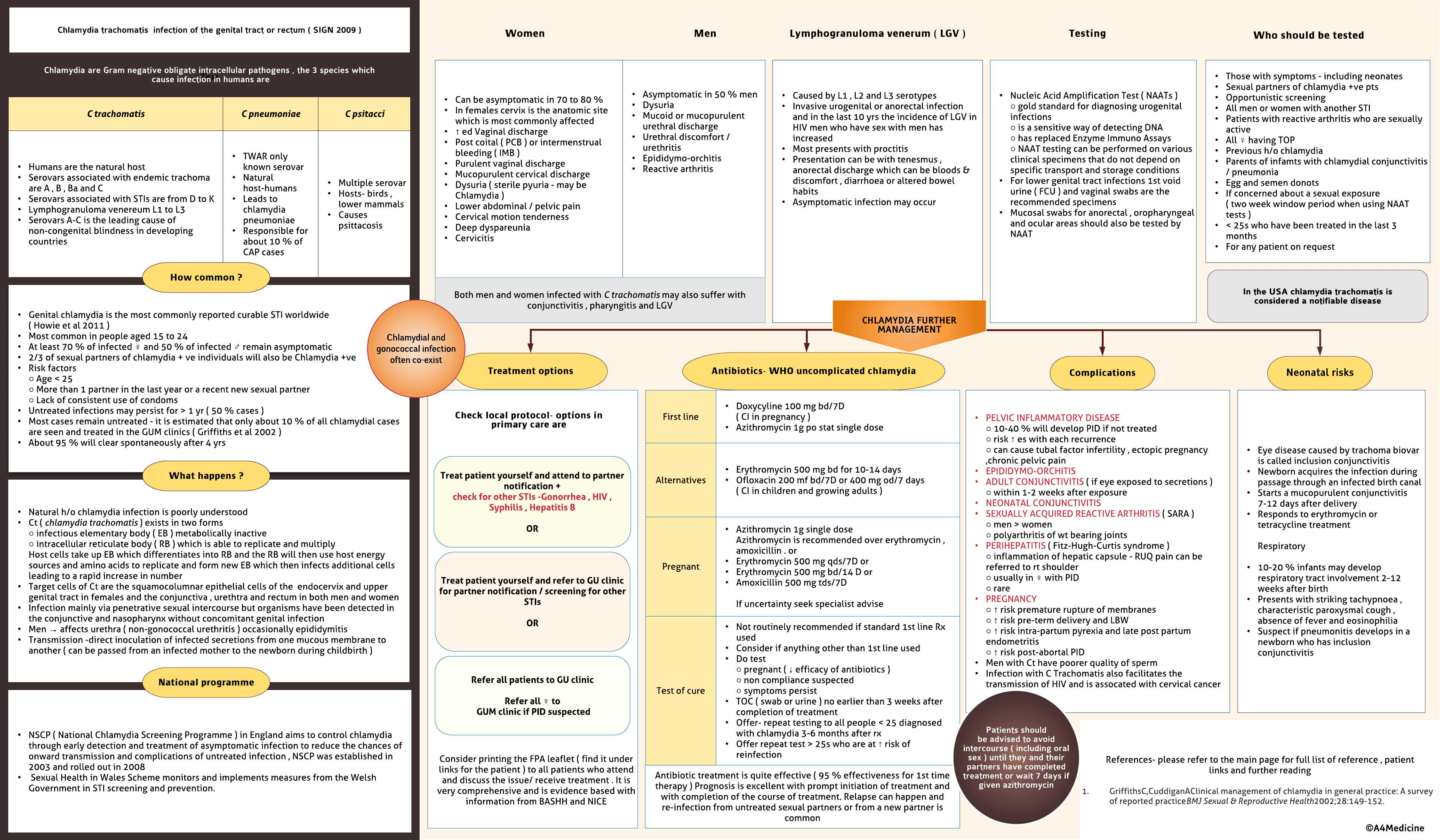
Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the genital tract or rectum ( SIGN 2009 ). Chlamydia are Gram-negative obligate intracellular pathogens, the 3 species which cause infection in humans are
Chlamydia trachomatis Humans are the natural host Serovars associated with endemic trachoma are A, B, Ba and C Serovars associated with STIs are D, E, F, G, H, I, J and K Lymphogranuloma venereum L1, L2 and L3 Genital chlamydia most commonly reported bacterial STI worldwide Men → affects urethra ( non-gonococcal urethritis ) ocassionally epididymitis Women →urethritis , cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease ( PVD ) Can also infect conjunctiva , rectum and nasopharynx Transmission -direct inoculation of infected secretions from one mucous membrane to another Infection has not ascended the upper genital tract -Uncomplicated infection Spread to upper genital tract- PID in womenEpididymo-orchitis in men-Complicated
Epidemiology-Most common in people aged 16-25 At least 70 % of infected and 50 % of infected remain asymptomatic 2/3 of sexual partners of chlamydia + ve individuals will also be Chlamydia +ve Risk factors○ Age < 25○ More than 1 partner in the last year or a recent new sexual partner○ Lack of consistent use of condoms Untreated infections may persist for > 1...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.