Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
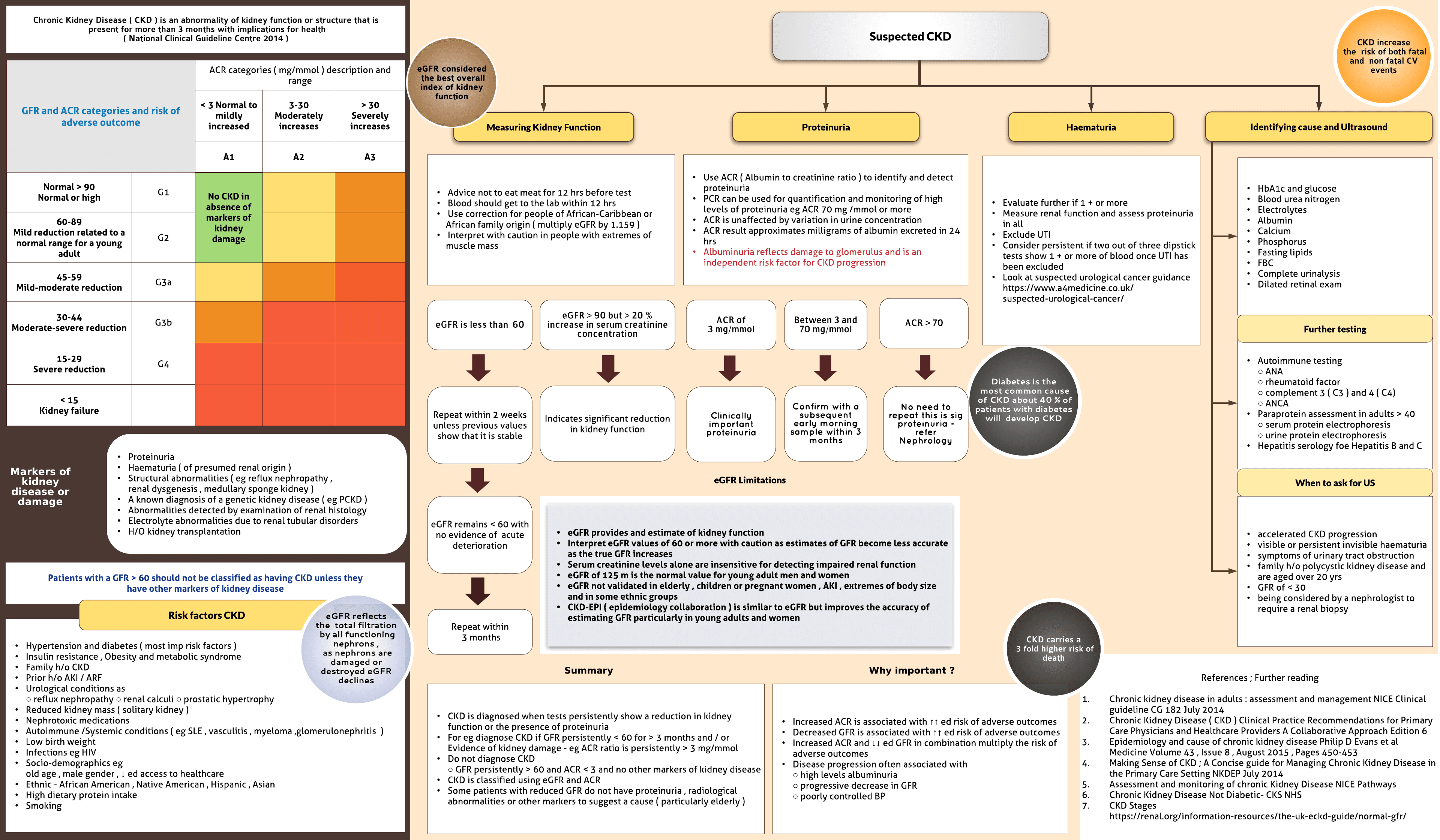
Chronic Kidney Disease ( CKD ) is an abnormality of kidney function or structure that is present for more than 3 months with implications for health ( National Clinical Guideline Centre 2014 )
eGFR reflects the total filtration by all functioning nephrons , as nephrons are damaged or destroyed eGFR declines
Markers of kidney disease or damage-Proteinuria Haematuria ( of presumed renal origin ) Structural abnormalities ( eg reflux nephropathy , renal dysgenesis , medullary sponge kidney ) A known diagnosis of a genetic kidney disease ( eg PCKD ) Abnormalities detected by examination of renal histology Electrolyte abnormalities due to renal tubular disorders H/O kidney transplantation. Patients with a GFR > 60 should not be classified as having CKD unless they have other markers of kidney disease
Risk factors- Hypertension and diabetes ( most imp risk factors ) Insulin resistance , Obesity and metabolic syndrome Family h/o CKD Prior h/o AKI / ARF Urological conditions as○ reflux nephropathy ○ renal calculi ○ prostatic hypertrophy Reduced kidney mass ( solitary kidney ) Nephrotoxic medications Autoimmune /Systemic conditions ( eg SLE , vasculitis , myeloma ,glomerulonephritis ) Low birth weight Infections eg HIV Sociodemographics egold age , male gender , ↓...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.