Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
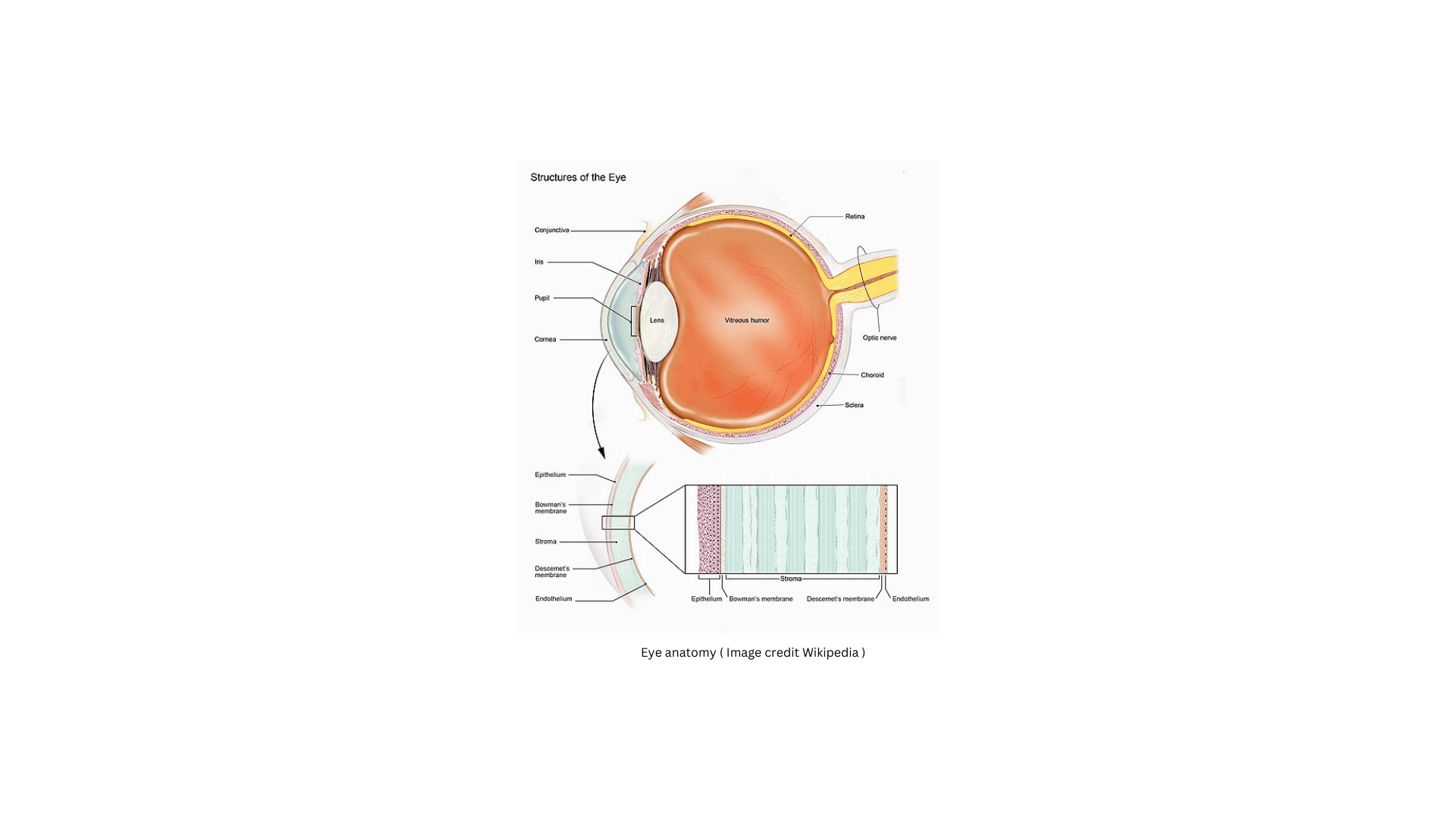
Corneal injury represents a significant clinical concern given the cornea's critical role as the foremost refractive element of the eye and its vulnerability as the most anterior structure. This delicate, transparent tissue, responsible for a substantial portion of the eye's focusing power, is susceptible to a spectrum of injuries—from minor abrasions to severe, sight-threatening trauma. The repercussions of corneal injury extend beyond the immediate physical damage, as even slight alterations in corneal structure can lead to profound visual disturbances, owing to its refractive significance.
Globally, corneal injuries contribute to visual impairment, with corneal opacification being a leading cause of blindness, second only to cataracts. This is particularly pronounced in developing regions, where it stands as a public health issue of considerable magnitude. Many instances of corneal blindness are both preventable and treatable, making the understanding and early management of corneal injuries a pivotal aspect of ophthalmic care.
Corneal abrasions, which involve the loss of the superficial epithelial layer, are among the most frequently encountered eye injuries in clinical practice. These are closely followed by corneal foreign bodies, which constitute a significant proportion of ocular traumas. The etiology of these conditions varies widely, with chemical injuries, workplace accidents, and vehicular incidents...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.