Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
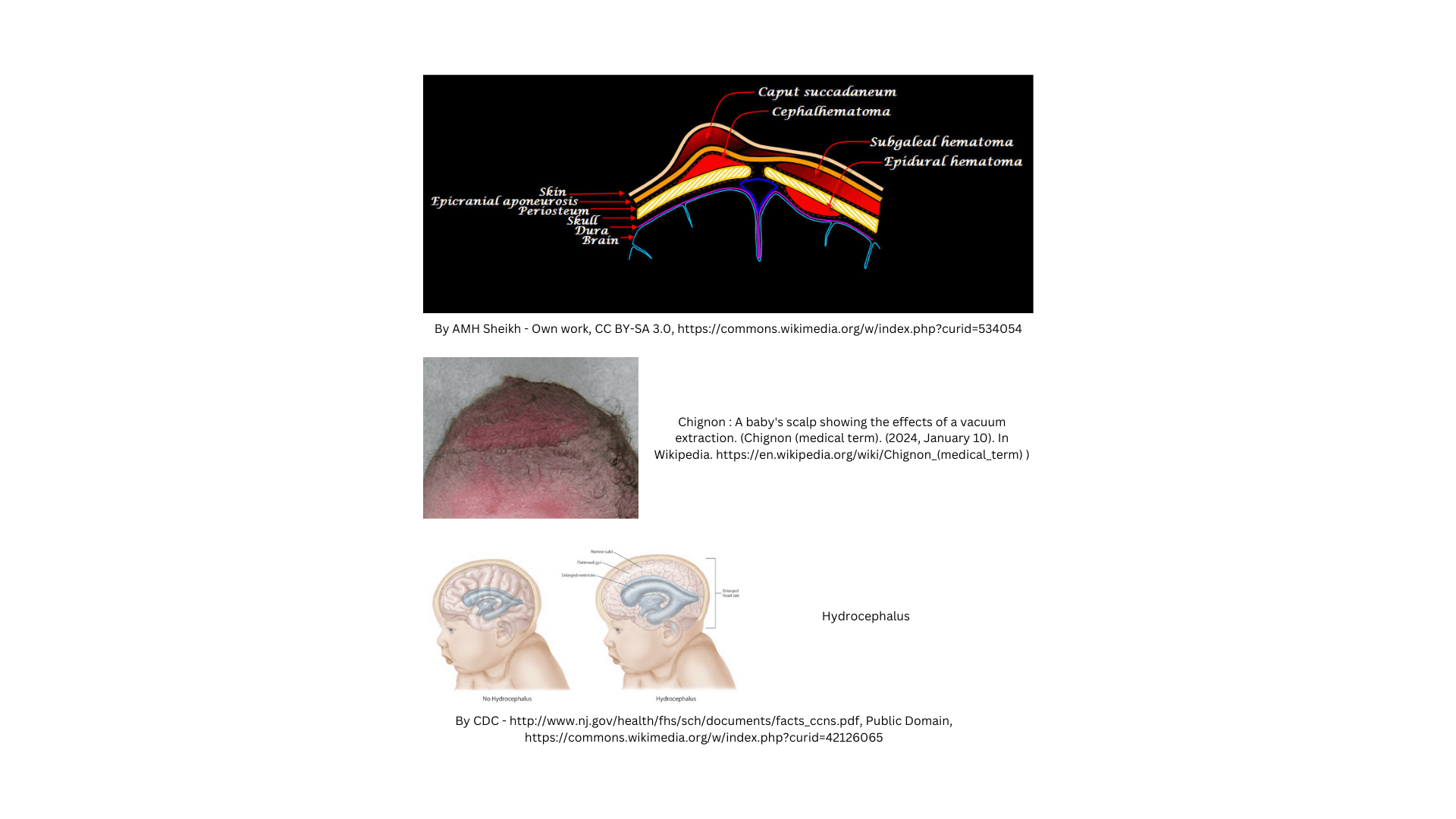
Cranial swellings in infants can be a source of concern for parents and a diagnostic challenge for primary care clinicians. These swellings can vary in aetiology, ranging from benign and self-limiting conditions to more serious underlying issues. Understanding the possible causes is crucial for appropriate management and referral.
This guide outlines several common causes of cranial swellings, including conditions such as caput succedaneum, cephalohematoma, craniosynostosis, and others like chignon, which occurs following vacuum extraction deliveries
| Cause | Characteristics | Primary Care Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Caput Succedaneum | • Swelling of the soft tissues of the scalp. • Develops during birth. • Often resolves within a few days. | • Usually benign. • Monitor for resolution. |
| Cephalohematoma | • Collection of blood between skull bone and its periosteum. • Does not cross suture lines. • Appears a few hours after birth. | • Monitor for resolution. • Assess for jaundice due to breakdown of red blood cells. |
| Craniosynostosis | • Premature fusion of one or more cranial sutures. • Abnormal head shape. • Can be associated with syndromes. | • Refer for specialist evaluation. • Possible need for surgical intervention. |
| Hydrocephalus | • Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. • Progressive head enlargement. • Fontanelles may be tense and bulging.... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.