Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
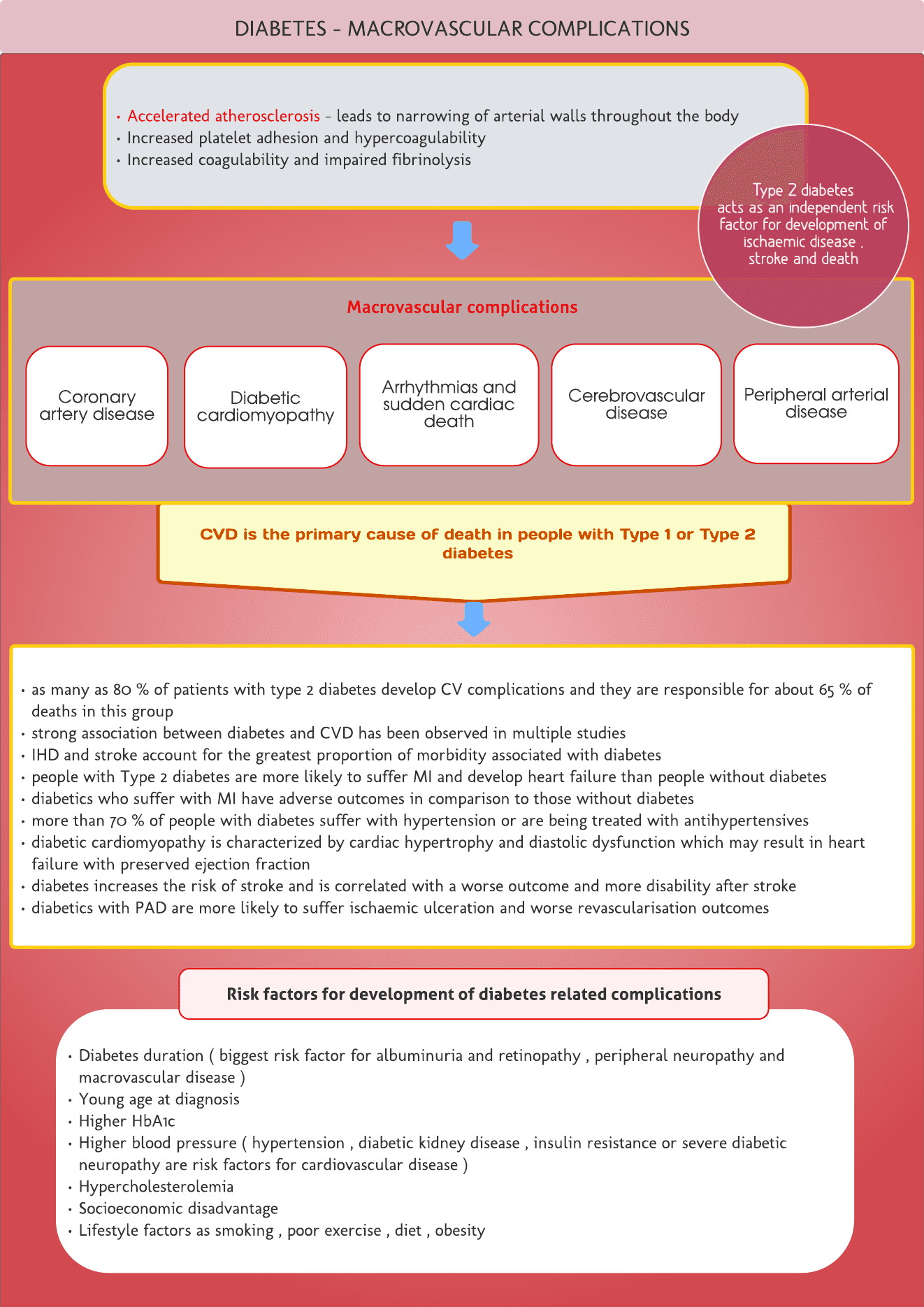
DIABETES - MACROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Accelerated atherosclerosis - leads to narrowing of arterial walls throughout the body Increased platelet adhesion and hypercoagulability Increased coagulability and impaired fibrinolysis.
as many as 80 % of patients with type 2 diabetes develop CV complications and they are responsible for about 65 % of deaths in this group strong association between diabetes and CVD has been observed in multiple studies IHD and stroke account for the greatest proportion of morbidity associated with diabetes people with Type 2 diabetes are more likely to suffer MI and develop heart failure than people without diabetes diabetics who suffer with MI have adverse outcomes in comparison to those without diabetes more than 70 % of people with diabetes suffer with hypertension or are being treated with antihypertensives diabetic cardiomyopathy is characterized by cardiac hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction which may result in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction diabetes increases the risk of stroke and is correlated with a worse outcome and more disability after stroke diabetics with PAD are more likely to suffer ischaemic ulceration and worse revascularisation outcomes.
Diabetes duration ( biggest risk factor for albuminuria and retinopathy , peripheral neuropathy and macrovascular disease ) Young age at...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.