Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
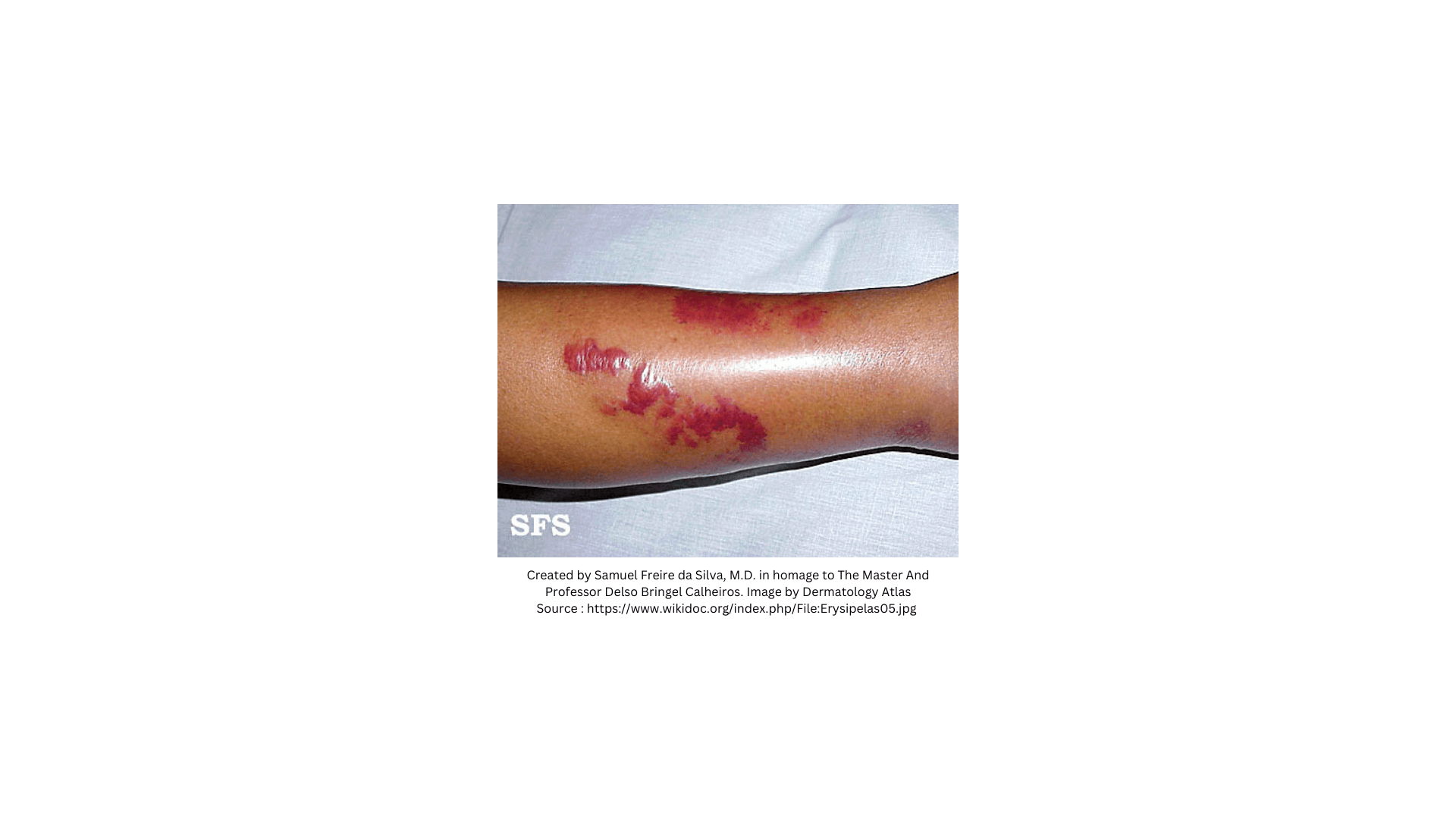
Erysipelas is a notable bacterial skin infection primarily characterized by a distinct, acute inflammation of the upper layers of the skin, particularly the dermis and hypodermis, along with the lymphatic vessels. This condition represents a specific type of cellulitis, but it is set apart by its superficial involvement and prominent, well-defined symptoms. The most common causative agent is Group A Streptococcus (GAS), and often, the pathogenesis of erysipelas is linked to the toxins produced by these bacteria, which contribute significantly to the clinical inflammation observed in patients.
The infection typically manifests with a sudden onset of symptoms, including rapidly progressing erythema (skin redness) and oedema , often accompanied by fever and other systemic signs. While erysipelas can affect various parts of the body, it is most frequently seen in the legs. However, occurrences in the face, arms, and upper thighs are also reported, especially in specific contexts like post-surgical recovery.
Erysipelas is distinctive for its acute and, at times, severe presentation, but it generally responds well to antibiotic therapy. Understanding its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and appropriate treatment is crucial, especially in primary care settings, where early recognition can lead to prompt and effective management, reducing the risk of complications and...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.