Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
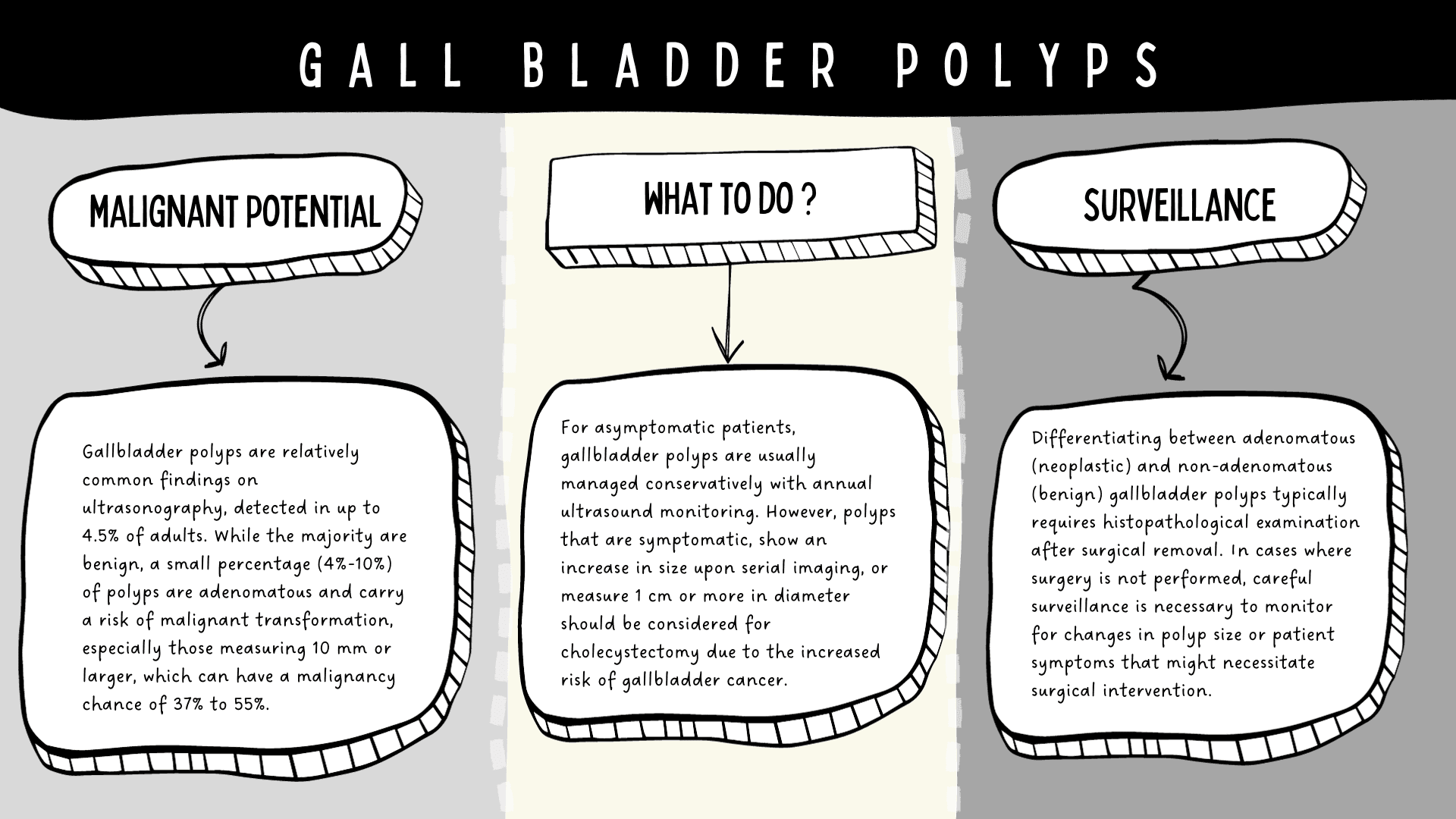
Gallbladder polyps are typically incidental findings during ultrasonographic examinations for other abdominal complaints. These lesions represent a spectrum of abnormalities ranging from benign cholesterolosis to adenomatous formations with potential malignant transformation. Managing gallbladder polyps is predicated on characteristics such as size, morphology, and patient symptomatology.
Polyps exceeding 1 cm in diameter warrant a more aggressive diagnostic and therapeutic approach due to an increased risk of gallbladder carcinoma.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Projections from the gallbladder wall into the lumen, which can be true neoplastic growths or non-neoplastic pseudopolyps such as cholesterol polyps. |
| Incidental Finding | Commonly diagnosed incidentally during routine abdominal ultrasound or following cholecystectomy for gallstones/biliary colic. |
| Symptoms | May be asymptomatic or present with symptoms akin to cholecystitis (e.g., right upper quadrant discomfort, nausea, and food intolerances). |
| Risk Factors for Neoplastic Polyps | Associated with genetic conditions such as familial polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers, Gardner syndrome, and hepatitis B. |
| Pseudopolyps | Often cholesterol-based, related to supersaturation of cholesterol in bile. Indicative of potential gallstone pathogenesis. |
| Management of Asymptomatic Polyps | Asymptomatic pseudo or cholesterol polyps are typically managed with yearly gallbladder ultrasounds due to their low malignant risk. |
| Indications for Cholecystectomy | Cholecystectomy is recommended if polyps enlarge on serial ultrasounds or if the patient becomes symptomatic.... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.