Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
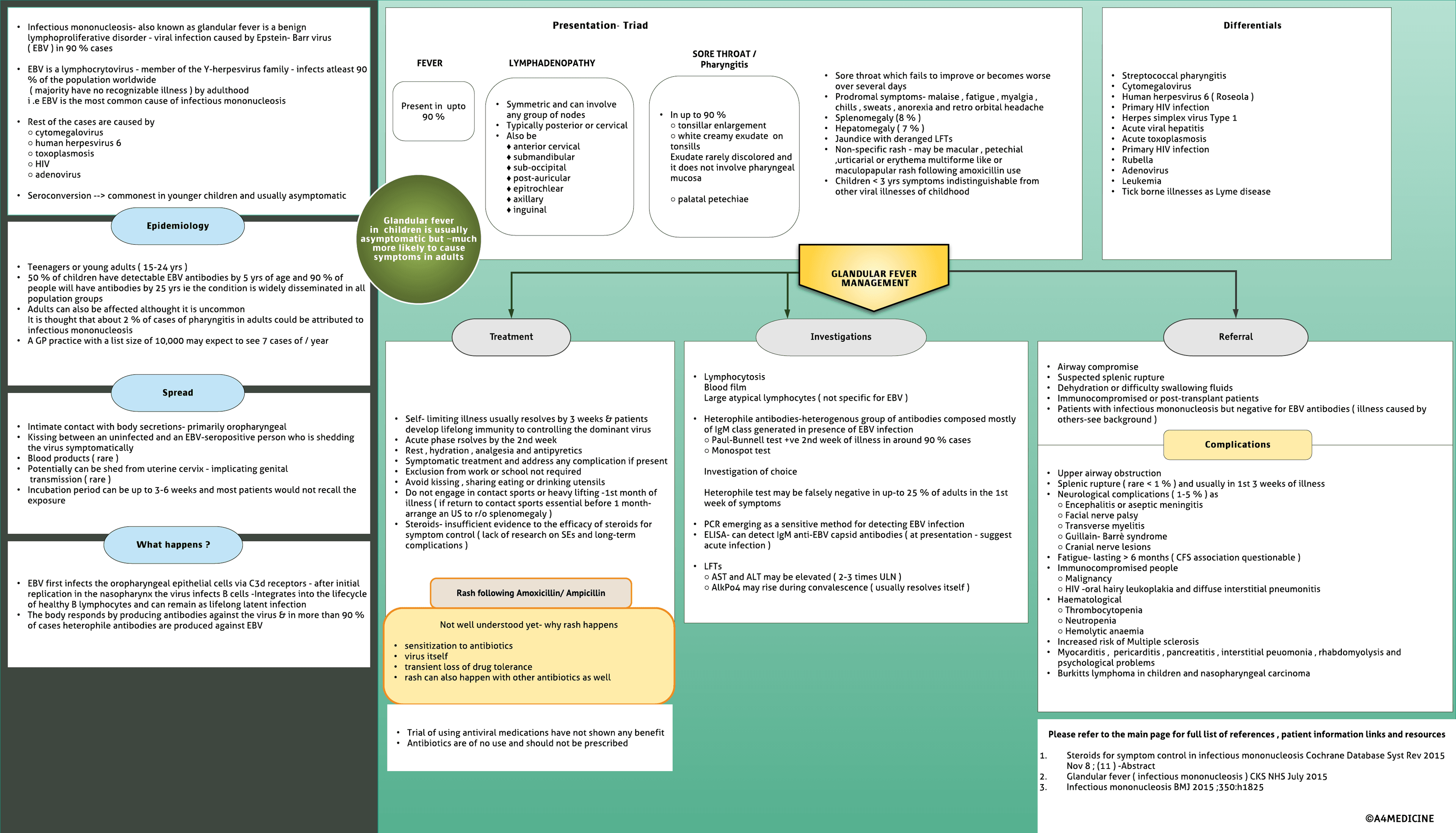
Infectious mononucleosis- also known as glandular fever is a benign lymphoproliferative disorder - viral infection caused by Epstein- Barr virus ( EBV ) in 90 % cases EBV is a lymphocrytovirus - member of the Y-herpesvirus family - infects atleast 90 % of the population worldwide ( majority have no recognizable illness ) by adulthood Rest of the cases are caused by○ cytomegalovirus○ human herpesvirus 6○ toxoplasmosis○ HIV○ adenovirus Seroconversion --> commonest in younger children and usually asymptomatic
Disease of primarily teenagers and young adults occurring in approximately 7 % with sore throat
As most population is positive for EBV special precautions against transmission are not necessary in most cases
Pathophysiology EBV first infects the oropharyngeal epithelial cells via C3d receptors After initial replication in the nasopharynx the virus infects B cells Integrates into the lifecycle of healthy B lymphocytes and can remain as lifelong latent infection Humoral response -Directed against EBV structural proteins structural response-T-lymphocyte cellular response - critical in control and determining the clinical expression of EBV infection
Epidemiology-Teenagers or young adults ( 15-24 yrs ) 50 % of children have detectable EBV antibodies by 5 yrs of age and 90 % of people will have antibodies by...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.