Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
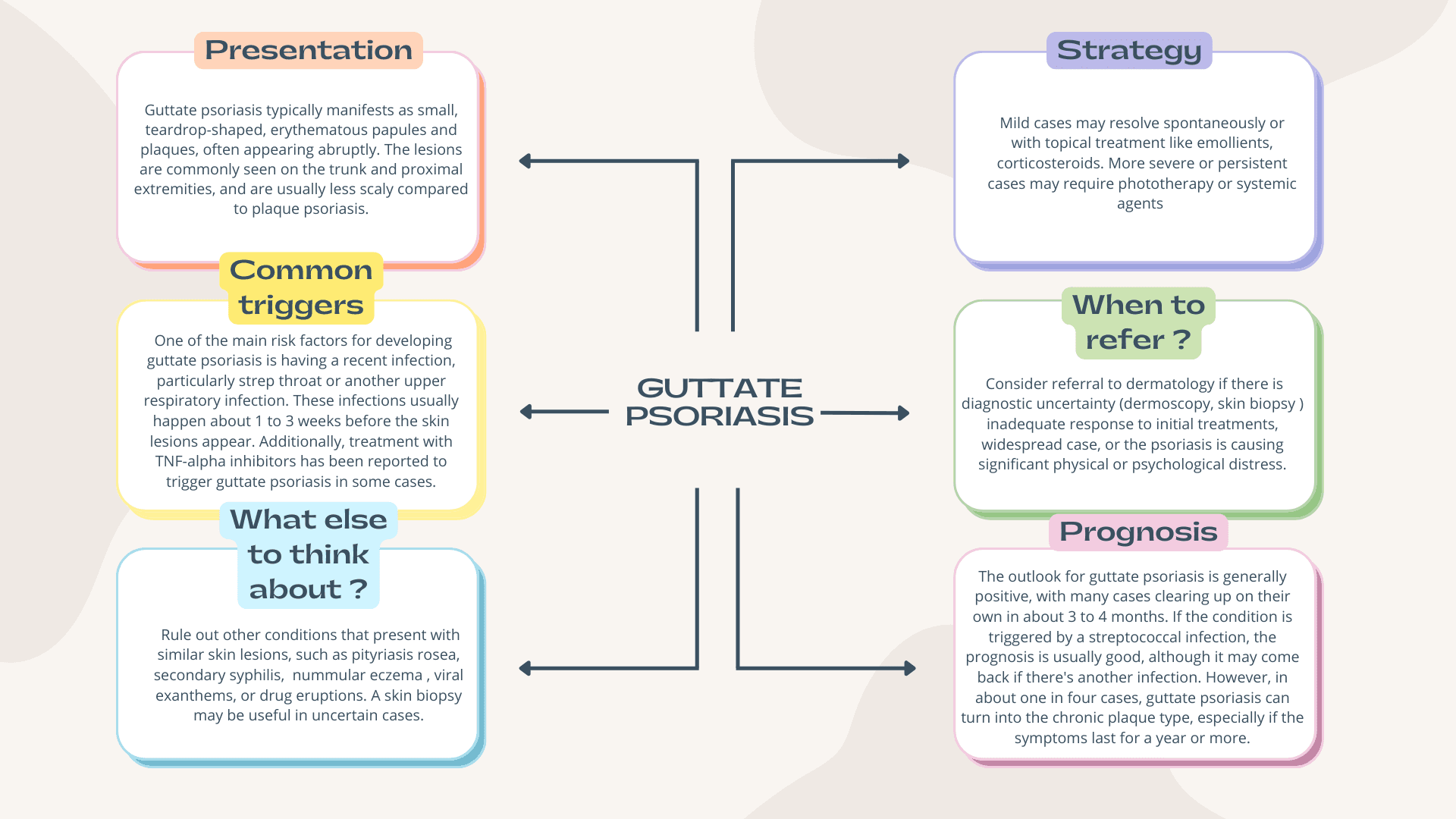
Guttate psoriasis is an acute form of psoriasis, commonly triggered by streptococcal infections and frequently seen in younger populations. Characterized by its distinct "drop-like" lesions, its management often necessitates a combined approach of topical treatments, lifestyle measures, and, in certain cases, specialized interventions. This table provides a comprehensive guide for primary care practitioners on its presentation, differential diagnoses, and recommended management strategies
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Acute form of psoriasis characterized by small, pink-red, scaly ‘raindrops’ distributed over the body. Originates from the Greek word "gutta", meaning droplet. |
| Epidemiology | - Typically affects individuals under 30. |
| - Contributes to about 2% of all psoriasis cases. | |
| - Approximately 8% of psoriasis patients develop this variant. | |
| Symptoms | - Papules: Numerous small, scattered papules and plaques, often described as "drop-like", typically 2 to 6 mm in size. |
| - Scaliness: Presence of scales, more noticeable on mature lesions, representing abnormal keratinization. | |
| - Distribution: Predominantly on trunk and limbs; facial, scalp, and ear lesions tend to be faint and short-lived. | |
| - Auspitz Sign: Pinpoint bleeding when the lesion's surface is removed, indicating elongated vessels in the dermal papillae with epidermal thinning. | |
| Clinical Features | - Onset: Acute manifestation over days. |
| - Koebner Phenomenon... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.