Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
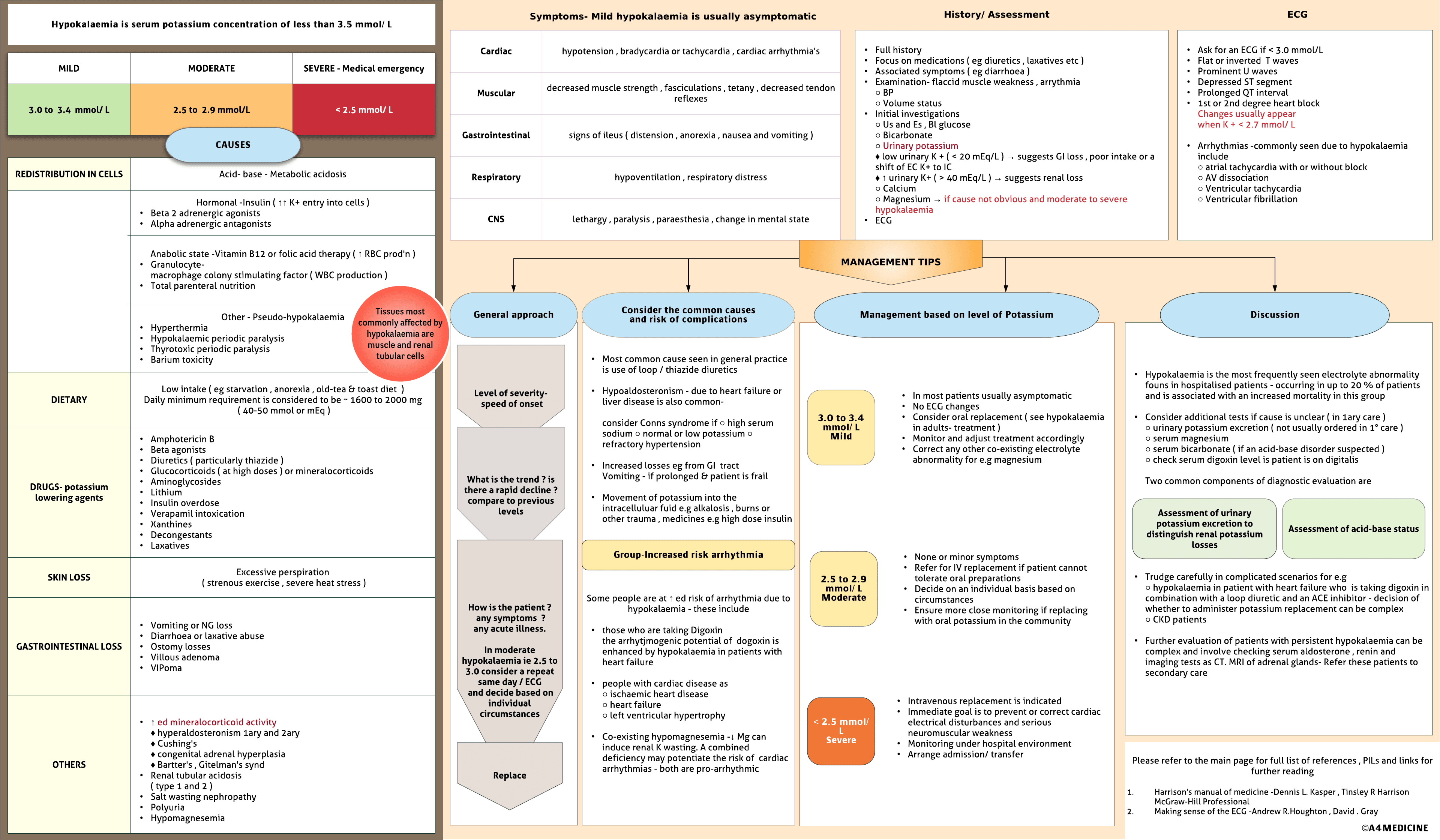
Hypokalaemia is serum potassium concentration of less than 3.5 mmol/ L. Mild hypokalemia is a K+ level of 3.0 to 3.4 mmol/ L. Moderate is 2.5 to 2.9 mmol/L and severe is > 2.5 mmol/L
Causes - redistribution in cells. Acid-base metabolic acidosis
Hormonal -Insulin ( ↑↑ K+ entry into cells ) Beta 2 adrenergic agonists Alpha adrenergic antagonists. Anabolic state -Vitamin B12 or folic acid therapy ( ↑ RBC prod'n ) Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor ( WBC production ) Total parenteral nutrition. Other - Pseudo-hypokalaemia Hyperthermia Hypokalaemic periodic paralysis Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis Barium toxicity
dietary -Low intake ( eg starvation , anorexia , old-tea & toast diet )Daily minimum requirement is considered to be ~ 1600 to 2000 mg ( 40-50 mmol or mEq )
Drugs -Amphotericin B Beta agonists Diuretics ( particularly thiazide ) Glucocorticoids ( at high doses ) or mineralocorticoids Aminoglycosides Lithium Insulin overdose Verapamil intoxication Xanthines Decongestants Laxatives
Skin loss -Excessive perspiration ( strenous exercise , severe heat stress )
gastrointestinal loss -Vomiting or NG loss Diarrhoe or laxative abuse Ostomy losses Villous adenoma VIPoma
Others - ↑ ed mineralocorticoid activity ♦ hyperaldosteronism 1ary and 2ary♦ Cushing's♦ congenital adrenal hyperplasia♦ Bartter's , Gitelman's synd Renal...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.