Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
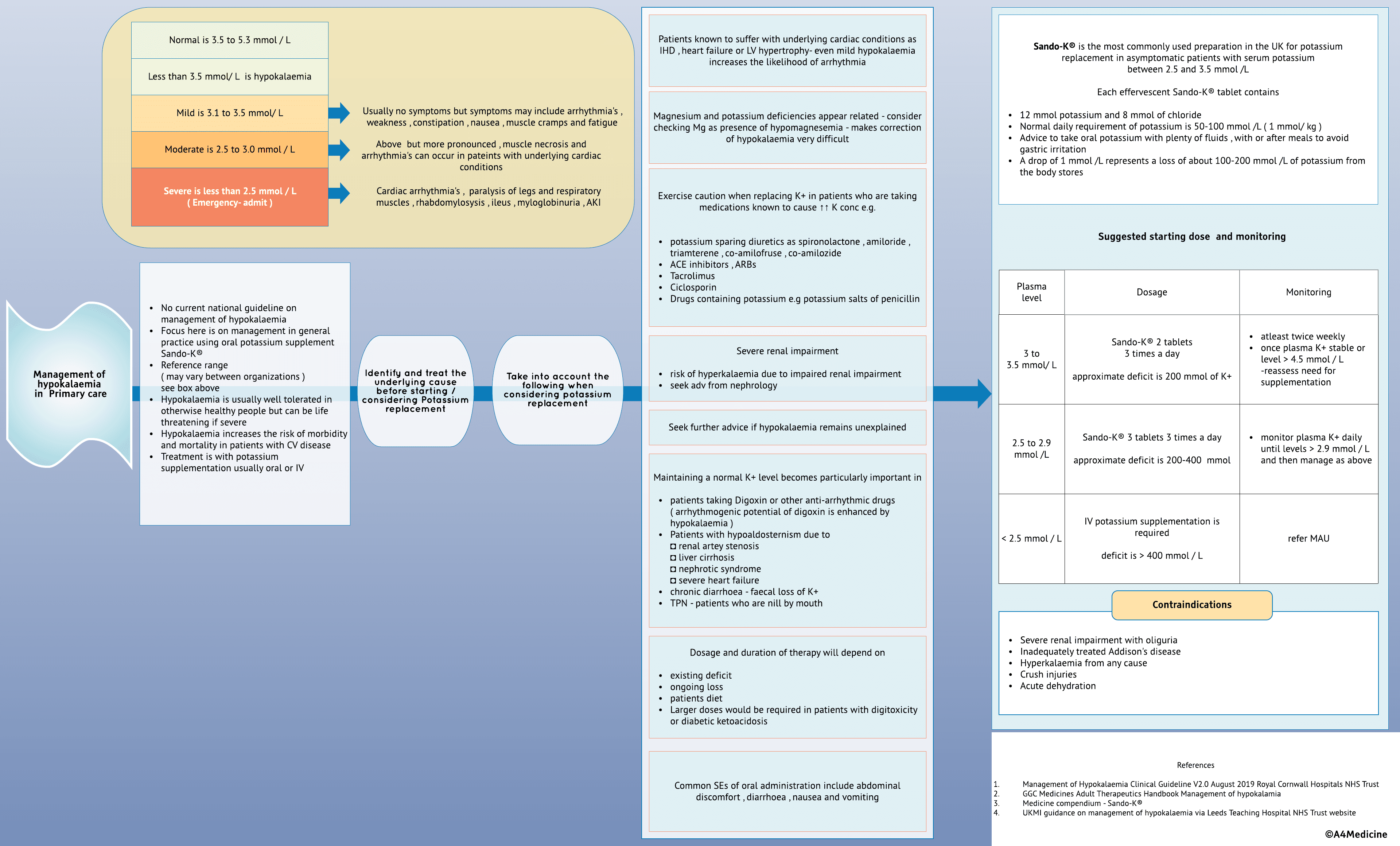
Management of hypokalaemia in Primary care-No current national guideline on management of hypokalaemia Focus here is on management in general practice using oral potassium supplement Sando-K® Reference range ( may vary between organizations )see box above Hypokalaemia is usually well tolerated in otherwise healthy people but can be life threatening if severe Hypokalaemia increases the risk of morbidity and mortality in patients with CV disease Treatment is with potassium supplementation usually oral or IV
Identify and treat the underlying cause before starting / considering Potassium replacement. Take into account the following when considering potassium replacement. Patients known to suffer with underlying cardiac conditions as IHD , heart failure or LV hypertrophy- even mild hypokalaemia increases the likelihood of arrhythmia
Magnesium and potassium deficiencies appear related - consider checking Mg as presence of hypomagnesemia - makes correction of hypokalaemia very difficult
Exercise caution when replacing K+ in patients who are taking medications known to cause ↑↑ K conc e.g. potassium sparing diuretics as spironolactone , amiloride , triamterene , co-amilofruse , co-amilozide ACE inhibitors , ARBs Tacrolimus Ciclosporin Drugs containing potassium e.g potassium salts of penicillin
Severe renal impairment risk of hyperkalaemia due to impaired renal impairment seek adv from nephrology....
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.