Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
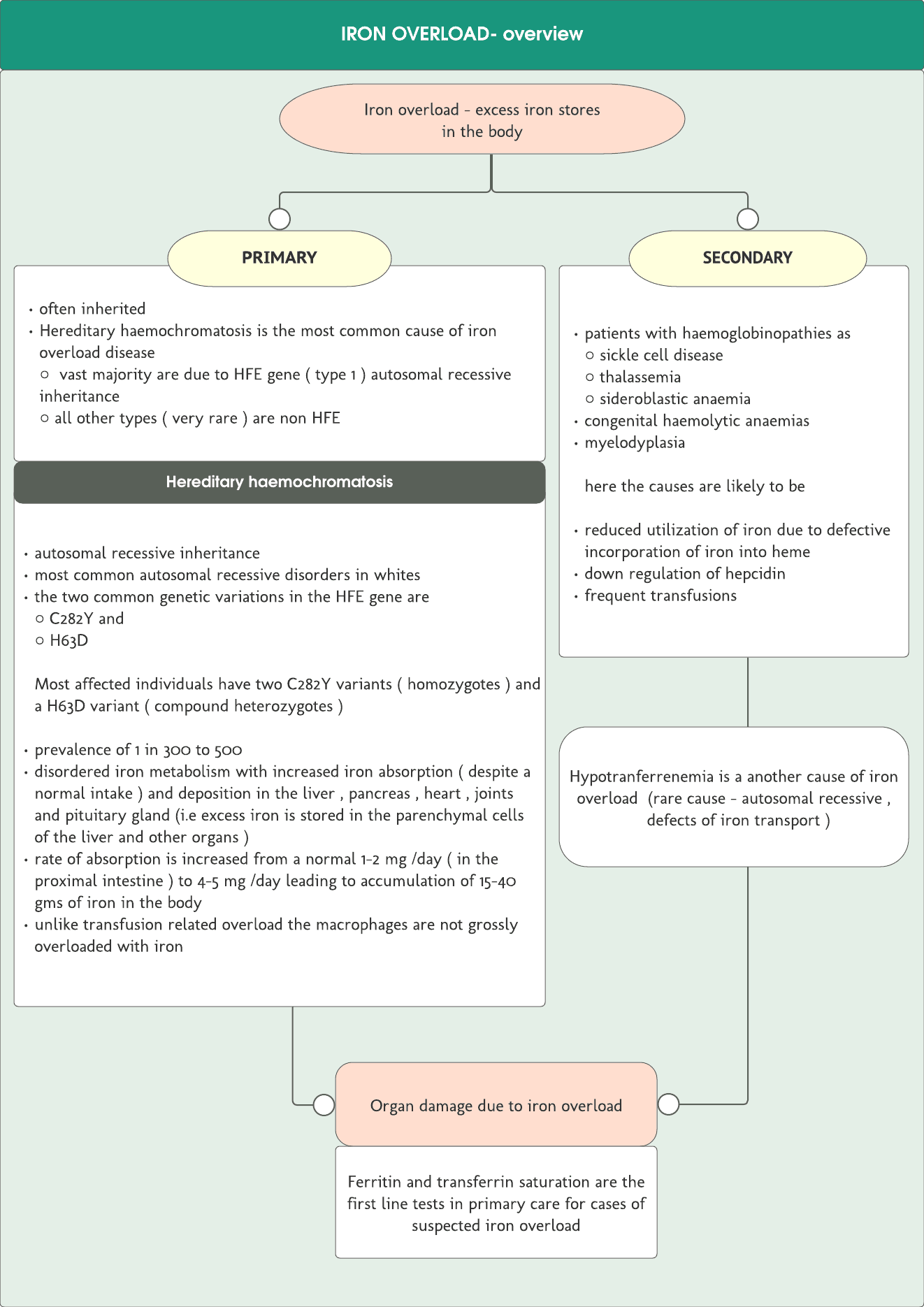
often inherited Hereditary haemochromatosis is the most common cause of iron overload disease ○ vast majority are due to HFE gene ( type 1 ) autosomal recessive inheritance○ all other types ( very rare ) are non HFE
autosomal recessive inheritance most common autosomal recessive disorders in whites the two common genetic variations in the HFE gene are○ C282Y and○ H63DMost affected individuals have two C282Y variants ( homozygotes ) and a H63D variant ( compound heterozygotes ) prevalence of 1 in 300 to 500 disordered iron metabolism with increased iron absorption ( despite a normal intake ) and deposition in the liver , pancreas , heart , joints and pituitary gland (i.e excess iron is stored in the parenchymal cells of the liver and other organs ) rate of absorption is increased from a normal 1-2 mg /day ( in the proximal intestine ) to 4-5 mg /day leading to accumulation of 15-40 gms of iron in the body unlike transfusion related overload the macrophages are not grossly overloaded with iron
patients with haemoglobinopathies as○ sickle cell disease○ thalassemia ○ sideroblastic anaemia congenital haemolytic anaemias myelodyplasiahere the causes are likely to be reduced utilization of iron due to defective...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.