Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
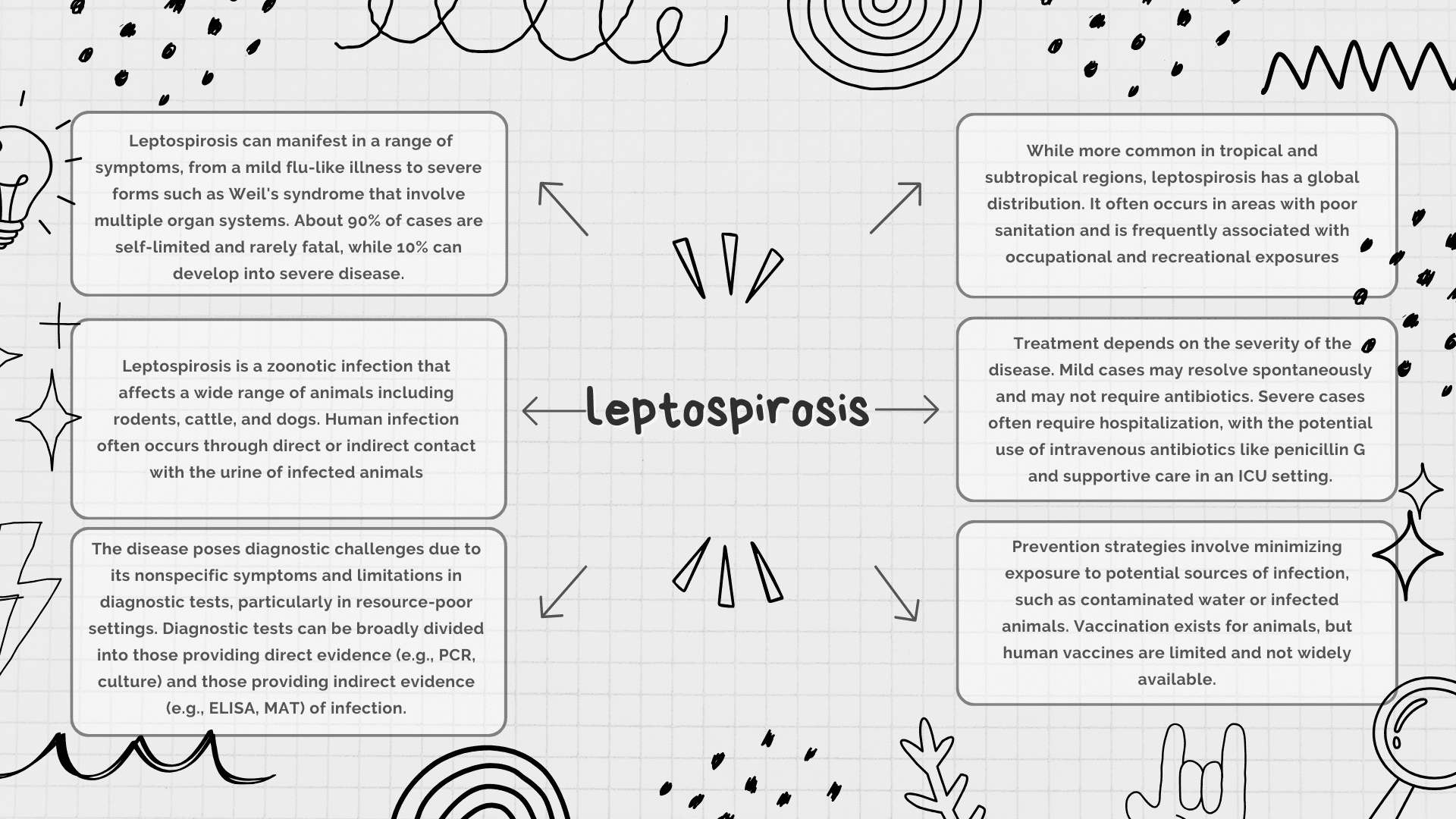
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that presents a significant public health challenge due to its wide range of clinical manifestations and diagnostic complexities. Caused by spirochetes from the genus Leptospira, the disease is a zoonotic infection affecting both humans and animals. The clinical spectrum of leptospirosis can vary dramatically, from mild, self-limited symptoms resembling flu-like illnesses to severe, life-threatening conditions involving multiple organ systems. Its diagnosis is equally challenging, complicated by limitations in diagnostic tests, particularly in resource-poor settings.
Effective management depends on early recognition and appropriate therapy, guided by the severity of the disease. With leptospirosis becoming increasingly prevalent, especially in tropical regions, an understanding of its clinical presentation, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options is essential for primary care clinicians and other healthcare providers.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Causative Agent | Leptospirosis is caused by spirochetes from the Leptospira genus. Pathogenic species are widespread and adapt to various host animals. |
| Molecular Pathogenesis | Once in the host, the bacteria disseminate hematogenously, predominantly targeting the kidneys. They colonize renal tubular epithelium without causing harm to the host animal. |
| Common Reservoirs | Small mammals like rats are the most significant. Large herbivores like cattle and domesticated animals like dogs are also noteworthy. |
| Uncommon Reservoirs | Leptospires have... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.