Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
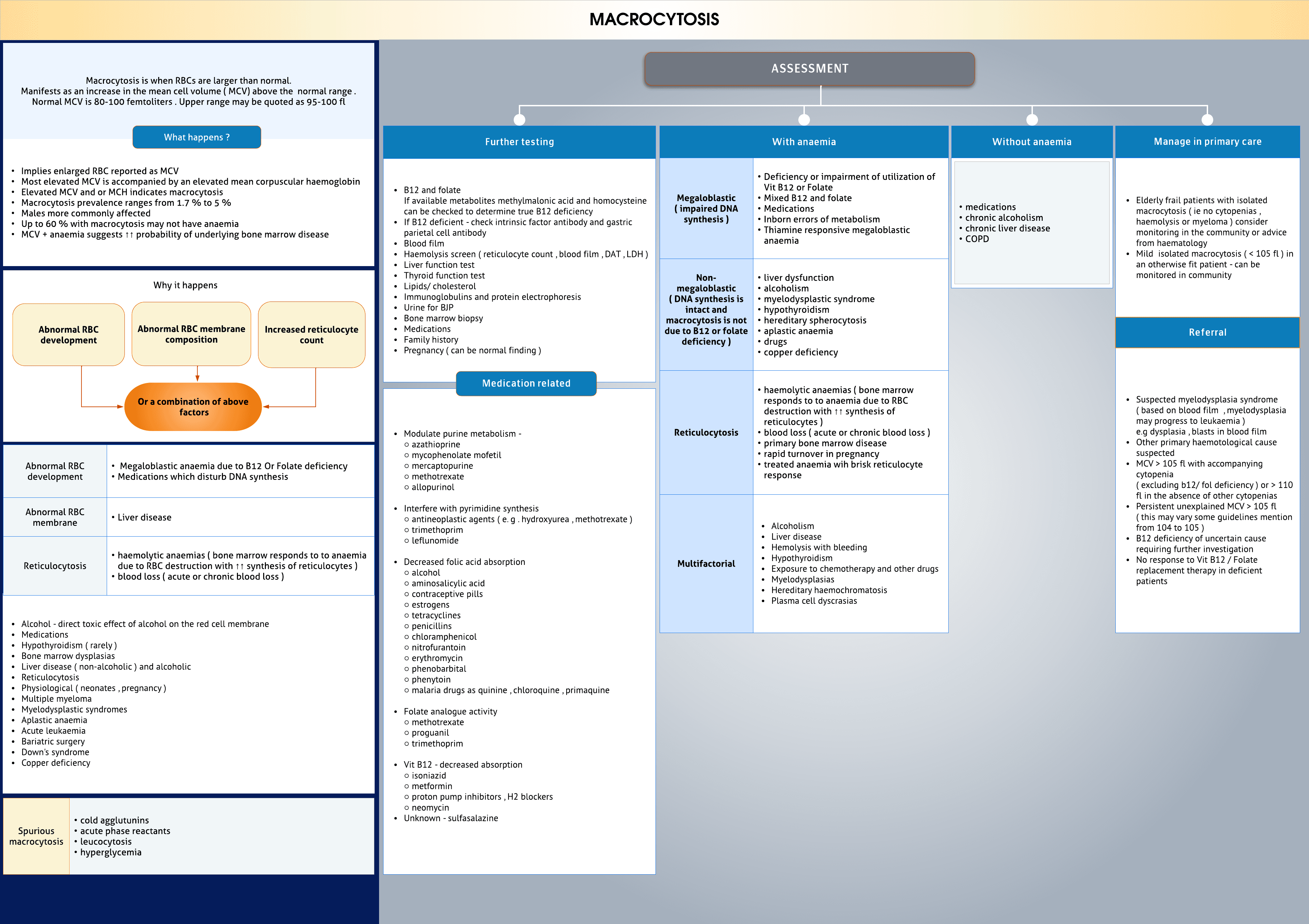
Macrocytosis -An increase in the mean cell volume ( MCV) above the normal range Upper range may be quoted as 95-100 fl. Prevalence ranges from 1.7 % to 5 % Up to 60-80 % with macrocytosis may not have anaemia
Main causes- Alcohol B12 and or folate deficiency Medications Hypothyroidism ( rarely ) Bone marrow dysplasias Liver disease ( non-alcoholic ) Reticulocytosis Physiological ( neonates , pregnancy ) Unexplained
Macrocytosis with anaemia - Alcoholism Liver disease Hemolysis with bleeding Hypothyroidism Folate or B12 deficiency Exposure to chemotherapy and other drugs Myelodysplasias Hereditary haemochromatosis Plasma cell dyscrasias
Macrocytosis without anaemia - Take detailed history Alcohol Drugs Tests ( particularly reticulocyte count and peripheral smear ) About 10 % cases may remain unexplained even after evaluation
Drug induced megaloblastic anaemia- Modulate purine metabolism -○ azathioprine○ mycophenolate mofetil○ mercaptopurine○ methotrexate○ allopurinol Interfere with pyrimidine synthesis○ antineoplastic agents ( e. g . hydroxyurea , methotrexate )○ trimethoprim○ leflunomide Decreased folic acid absorption○ alcohol○ aminosalicylic acid○ contraceptive pills○ estrogens○ tetracyclines○ penicillins ○ chloramphenicol○ nitrofurantoin○ erythromycin○ phenobarbital○ phenytoin○ malaria drugs as quinine , chloroquine , primaquine Folate analogue activity○ methotrexate○ proguanil○ trimethoprim Vit B12 - decreased absorption○ isoniazid○ metformin○ proton pump inhibitors , H2 blockers○ neomycin...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.