Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
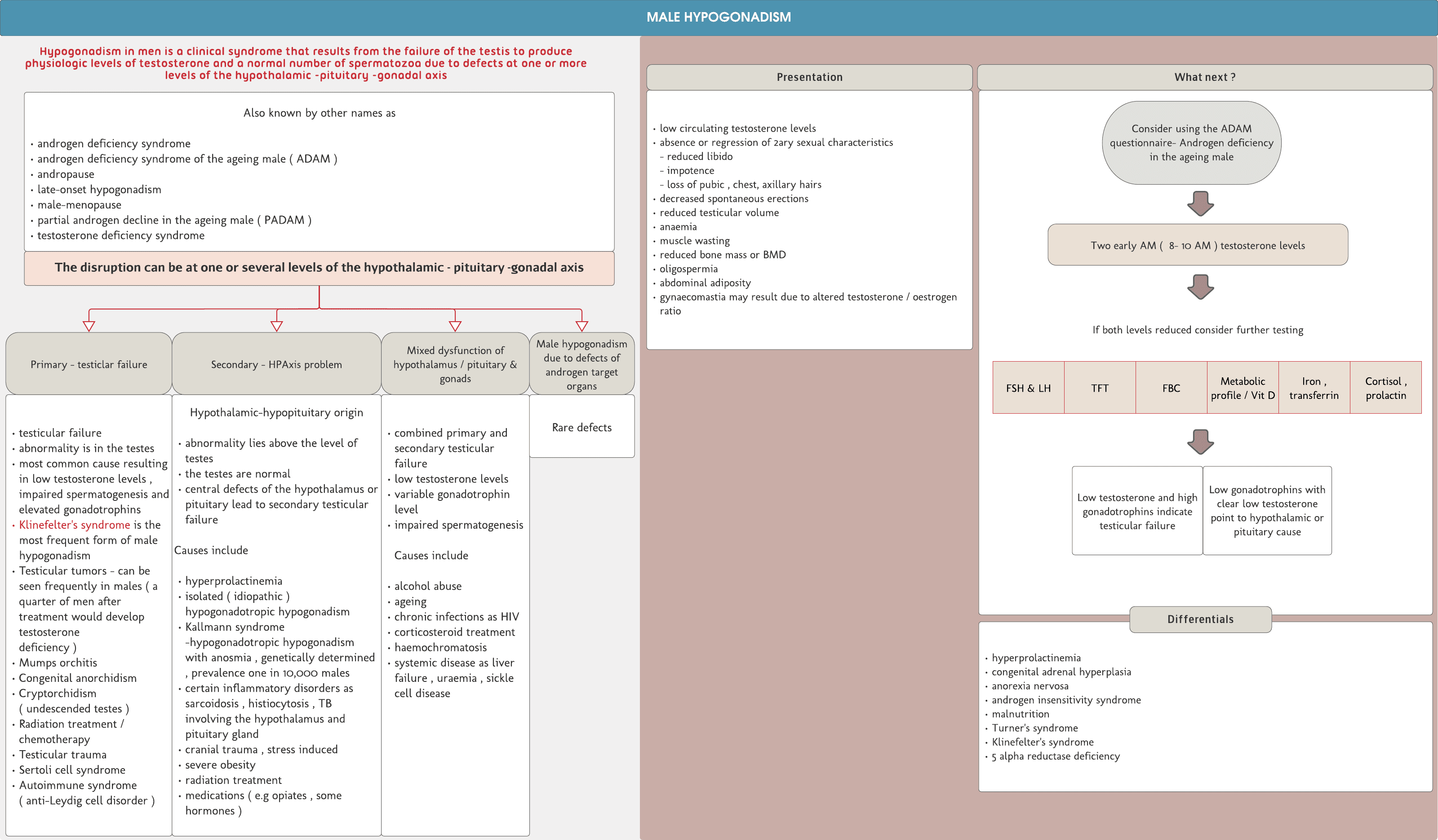
The disruption can be at one or several levels of the hypothalamic - pituitary -gonadal axis
Also known by other names as androgen deficiency syndrome androgen deficiency syndrome of the ageing male ( ADAM ) andropause late-onset hypogonadism male-menopause partial androgen decline in the ageing male ( PADAM ) testosterone deficiency syndrome
Primary- testicular failure abnormality is in the testes most common cause resulting in low testosterone levels , impaired spermatogenesis and elevated gonadotrophins Klinefelter’s syndrome is the most frequent form of male hypogonadism Testicular tumors - can be seen frequently in males ( a quarter of men after treatment would develop testosterone deficiency ) Mumps orchitis Congenital anorchidism Cryptorchidism Radiation treatment / chemotherapy Testicular trauma Sertoli cell syndrome Autoimmune syndrome ( anti-Leydig cell disorder )
Secondary- Hypothalamic-hypopituitary origin abnormality lies above the level of testes central defects of the hypothalamus or pituitary lead to secondary testicular failure Causes include hyperprolactinemia isolated ( idiopathic ) hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Kallmann syndrome -hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia , genetically determined , prevalence one in 10,000 males cranial trauma radiation treatment medications
Mixed dysfunction of hypothalamus / pituitary and gonads - combined primary and secondary testicular failure low testosterone levels variable gonadotrophin level impaired spermatogenesisCauses...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.