Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
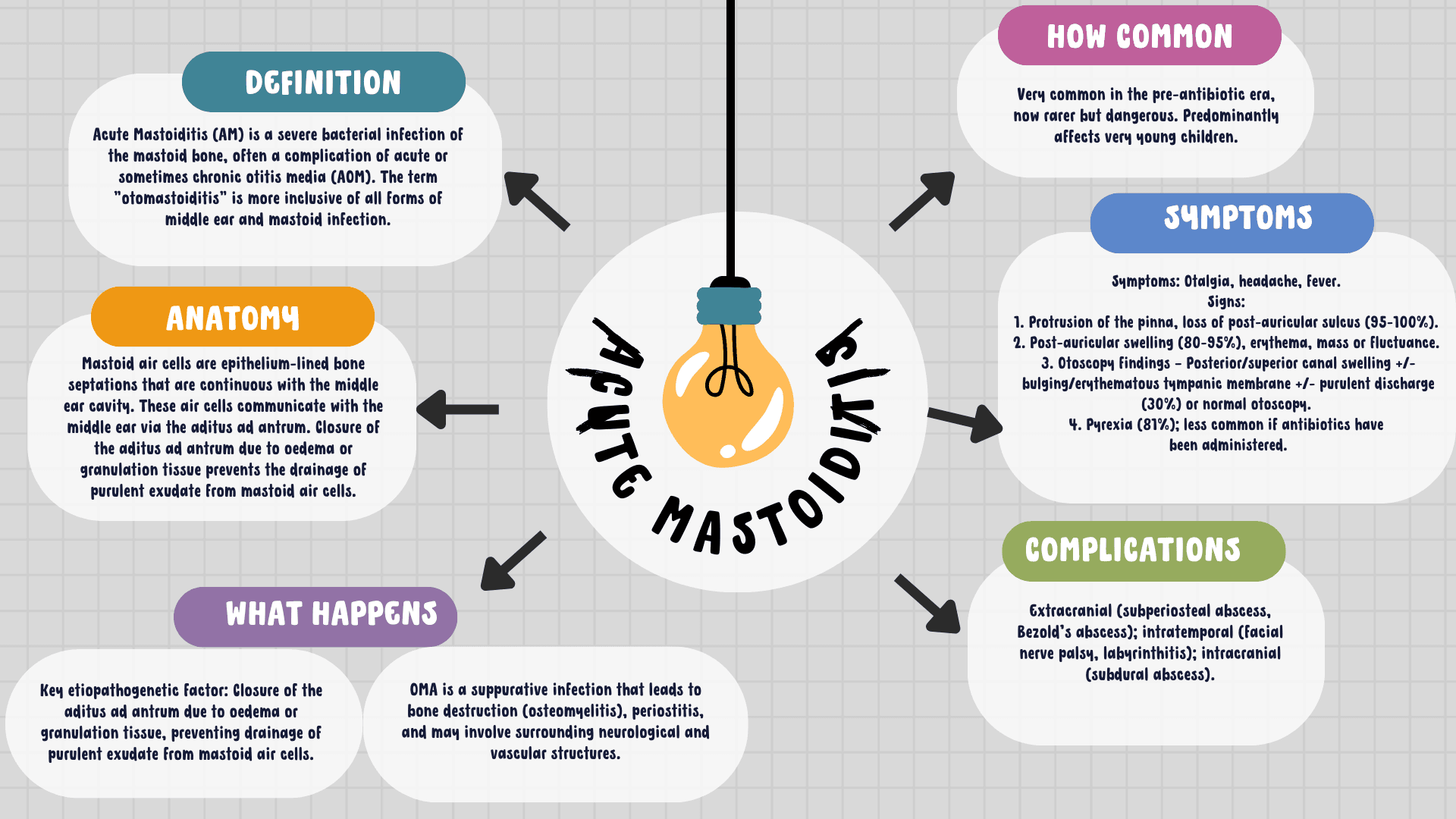
The following table provides a comprehensive yet concise overview of acute mastoiditis, a severe bacterial infection of the mastoid bone that is often a complication of acute or sometimes chronic otitis media. Designed to be a quick reference guide, the table covers essential topics such as anatomy, aetiology, prevalence, pathophysiology, key pathogens, risk factors, clinical presentation, treatment options, complications, and potential sequelae if left untreated. It is intended for clinicians and medical students who need an in-depth understanding of this condition for effective diagnosis and management.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Acute Mastoiditis (AM) is a severe bacterial infection of the mastoid bone, often a complication of acute or sometimes chronic otitis media (AOM). The term "otomastoiditis" is more inclusive of all forms of middle ear and mastoid infection. |
| Anatomy | Mastoid air cells are epithelium-lined bone septations that are continuous with the middle ear cavity. These air cells communicate with the middle ear via the aditus ad antrum. Closure of the aditus ad antrum due to oedema or granulation tissue prevents the drainage of purulent exudate from mastoid air cells. |
| Aetiology | Key etiopathogenetic factor: Closure of the aditus ad antrum due to oedema or granulation tissue, preventing drainage of purulent exudate from... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.