Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
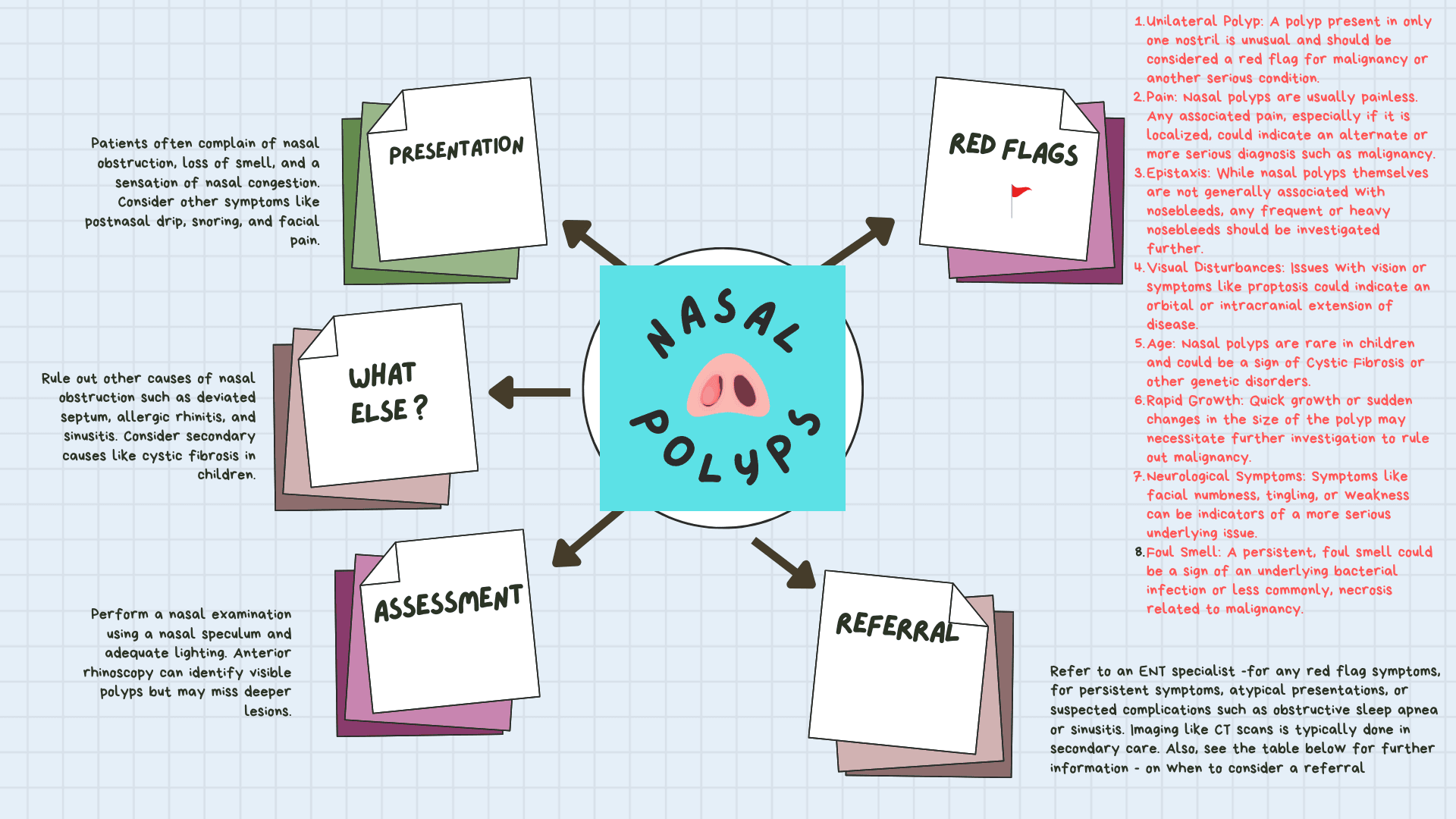
Nasal polyps represent a common but challenging clinical scenario for primary care physicians.
These benign growths often arise in the milieu of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), with two predominant clinical phenotypes:
◘ CRS with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and
◘ CRS without nasal polyps (CRSsNP).
Given the prevalence of CRSwNP in approximately 25-30% of CRS patients, it is imperative for primary care clinicians to possess a thorough understanding of this condition for effective diagnosis and management. This condensed table aims to provide primary care clinicians with an invaluable resource for understanding, diagnosing, and managing nasal polyps.
| Category | Description, Diagnostic Criteria, & Clinical Assessment | Management & Advanced Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Presentation & Diagnosis | • Nasal polyps should be suspected in patients with symptoms like nasal obstruction, facial or nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and hyposmia—the cardinal symptoms of CRS. • Additional symptoms may include epistaxis, postnasal drip, headaches, and snoring. • The presence of aspirin sensitivity or asthma may indicate Samter's triad. • Symptoms appearing unilaterally or accompanied by a history of epistaxis, chronic otitis media, recurrent bronchitis, and pneumonia warrant investigation into other etiologies. • Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on symptoms and either anterior rhinoscopy or nasal endoscopy. PNS CT scans may further... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.