Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
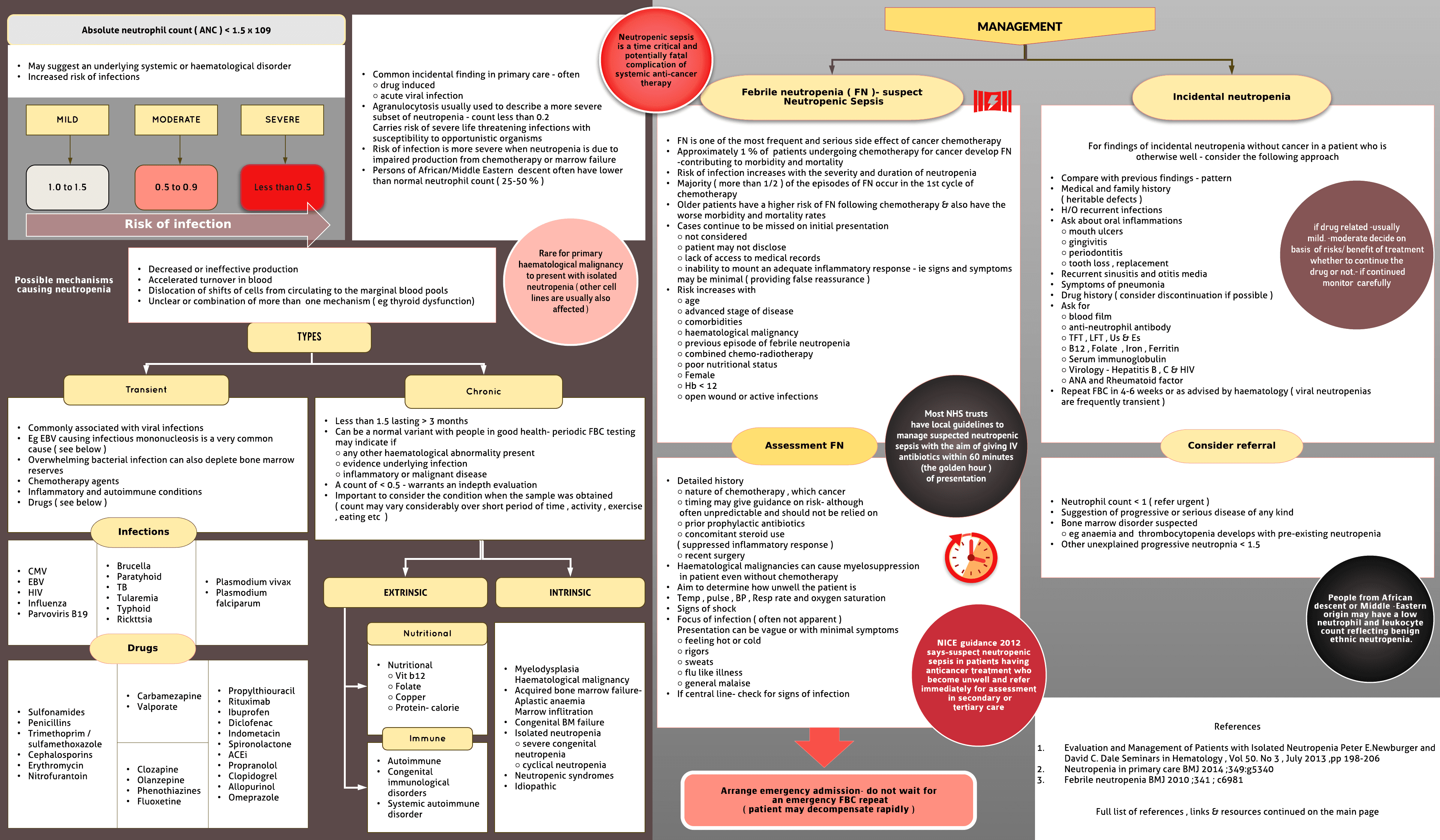
Absolute neutrophil count ( ANC ) < 1.5 x 109 May suggest an underlying systemic or haematological disorder Increased risk of infections
Common incidental finding in primary care - often○ drug induced○ acute viral infection Agranulocytosis usually used to describe a more severe subset of neutropenia - count less than 0.2 Carries risk of severe life threatening infections with susceptibility to opportunistic organisms Risk of infection is more severe when neutropenia is due to impaired production from chemotherapy or marrow failure Persons of African descent often have lower than normal neutrophil count
Decreased or ineffective production Accelerated turnover in blood Dislocation of shifts of cells from circulating to the marginal blood pools Unclear or combination of more than one mechanism ( eg thyroid dysfunction) .Rare for primary haematological malignancy to present with isolated neutropenia ( other cell lines are usually also affected )
Transient- Commonly associated with viral infections Eg EBV causing infectious mononucleosis is a very common cause ( see below ) Overwhelming bacterial infection can also deplete bone marrow reserves Chemotherapy agents Inflammatory and autoimmune conditions Drugs ( see below )
chronic- Less than 1.5 lasting > 3 months Can be a normal variant with people in good...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.