Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
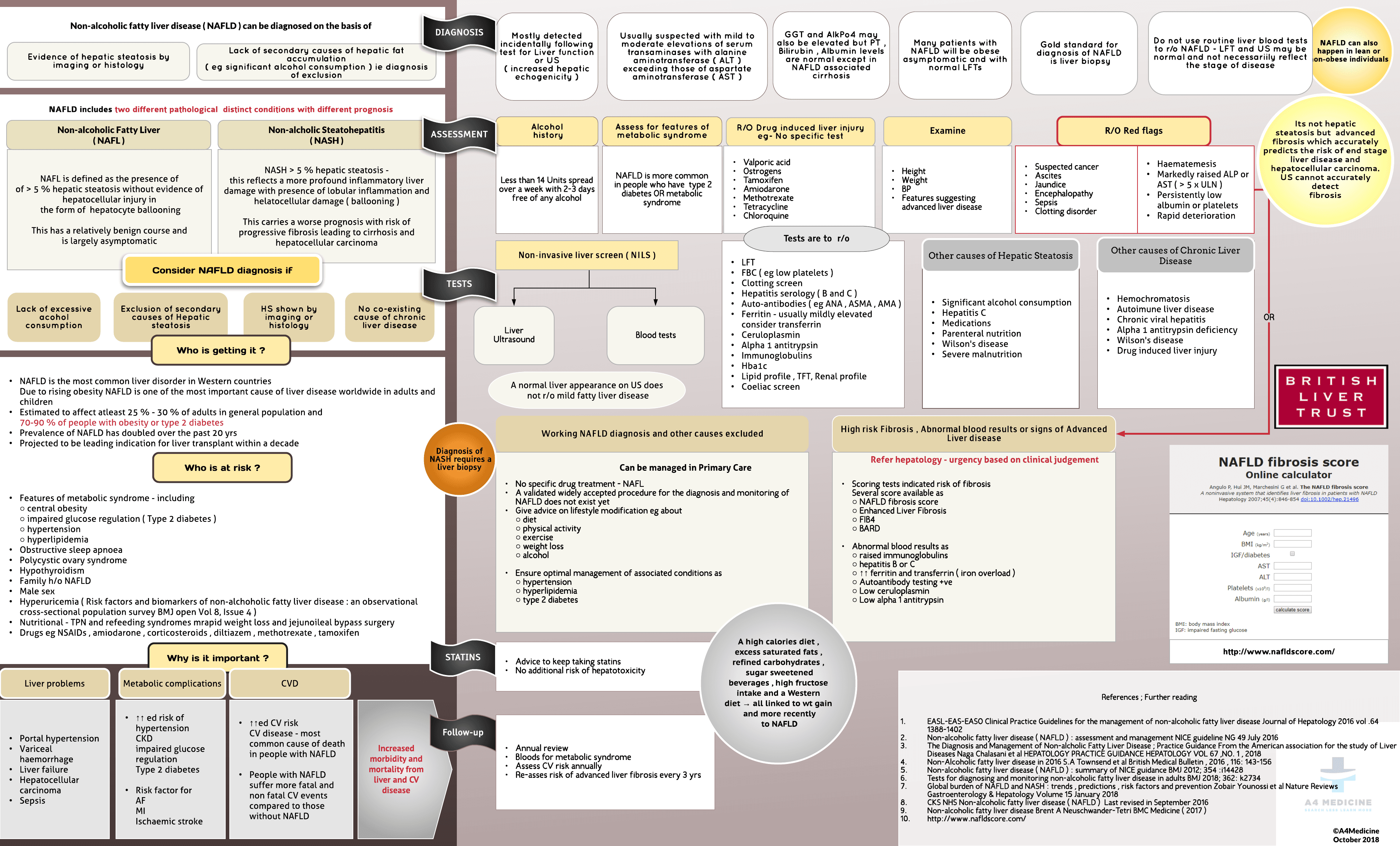
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD ) can be diagnosed on the basis of Evidence of hepatic steatosis by imaging or histology Lack of secondary causes of hepatic fat accumulation ( eg significant alcohol consumption ) ie diagnosis of exclusion
NAFL-NAFL is defined as the presence of of > 5 % hepatic steatosis without evidence of hepatocellular injury in the form of hepatocyte ballooningThis has a relatively benign course and is largely asymptomatic NASH- NASH > 5 % hepatic steatosis - this reflects a more profound inflammatory liver damage with presence of lobular inflammation and helatocellular damage ( ballooning )This carries a worse prognosis with risk of progressive fibrosis leading to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
NAFLD is the most common liver disorder in Western countriesDue to rising obesity NAFLD is one of the most important cause of liver disease worldwide in adults and children Estimated to affect atleast 25 % - 30 % of adults in general population and70-90 % of people with obesity or type 2 diabetes Prevalence of NAFLD has doubled over the past 20 yrs Projected to be leading indication for liver transplant within a decade
Features of metabolic syndrome - including○ central obesity○ impaired glucose regulation...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.