Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
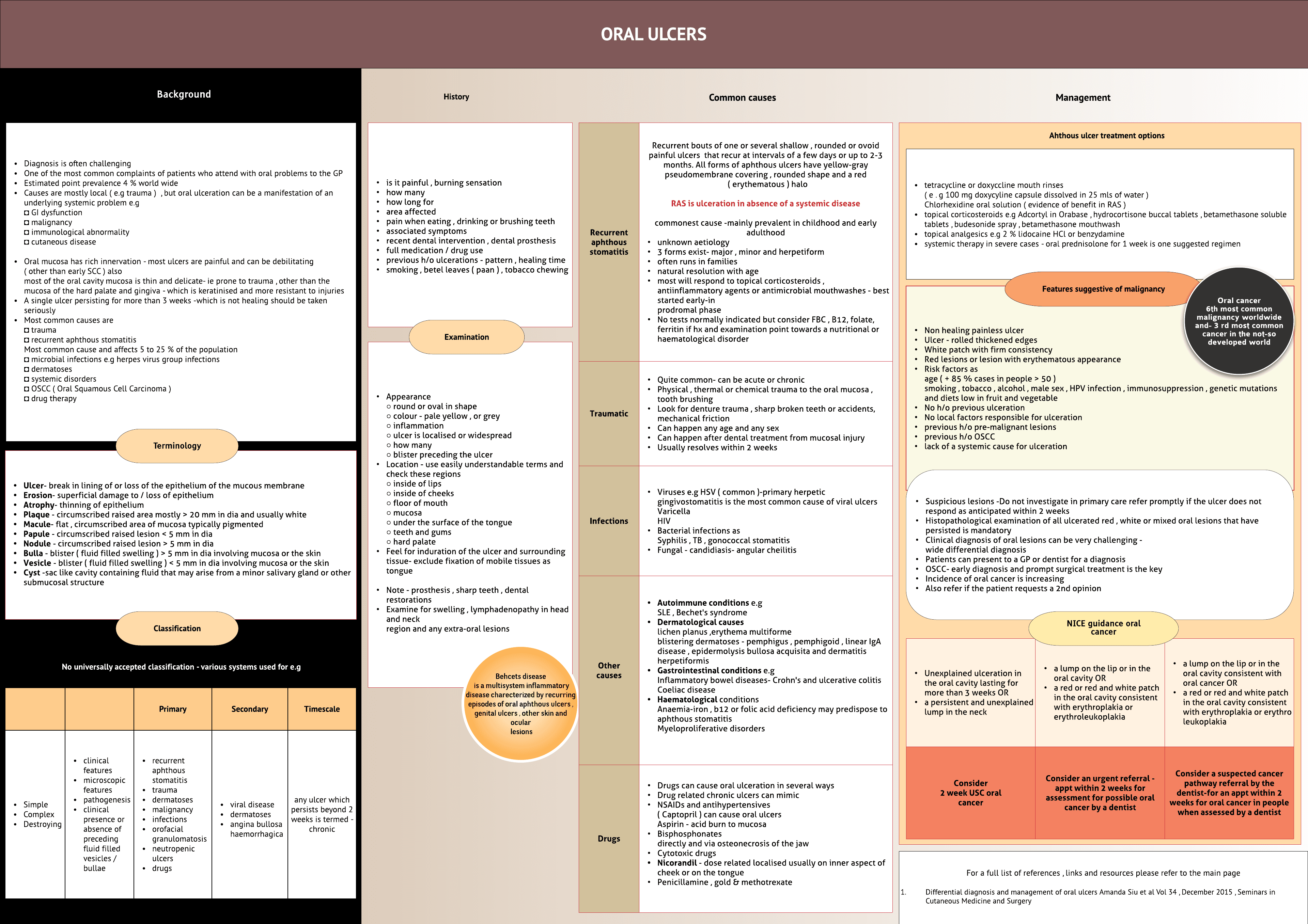
Diagnosis is often challenging One of the most common complaints of patients who attend with oral problems to the GP Estimated point prevalence 4 % world wide Causes are mostly local ( e.g trauma ) , but oral ulceration can be a manifestation of an underlying systemic problem e.g ◘ GI dysfunction◘ malignancy◘ immunological abnormality◘ cutaneous disease Oral mucosa has rich innervation - most ulcers are painful and can be debilitating( other than early SCC ) alsomost of the oral cavity mucosa is thin and delicate- ie prone to trauma , other than the mucosa of the hard palate and gingiva - which is keratinised and more resistant to injuries A single ulcer persisting for more than 3 weeks -which is not healing should be taken seriously Most common causes are◘ trauma◘ recurrent aphthous stomatitisMost common cause and affects 5 to 25 % of the population◘ microbial infections e.g herpes virus group infections◘ dermatoses◘ systemic disorders◘ OSCC ( oral SCC )◘ drug therapy
Ulcer- break in lining of or loss of the epithelium of the mucous membrane Erosion- superficial damage to / loss of epithelium Atrophy- thinning of epithelium Plaque - circumscribed raised area mostly > 20 mm in dia...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.