Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
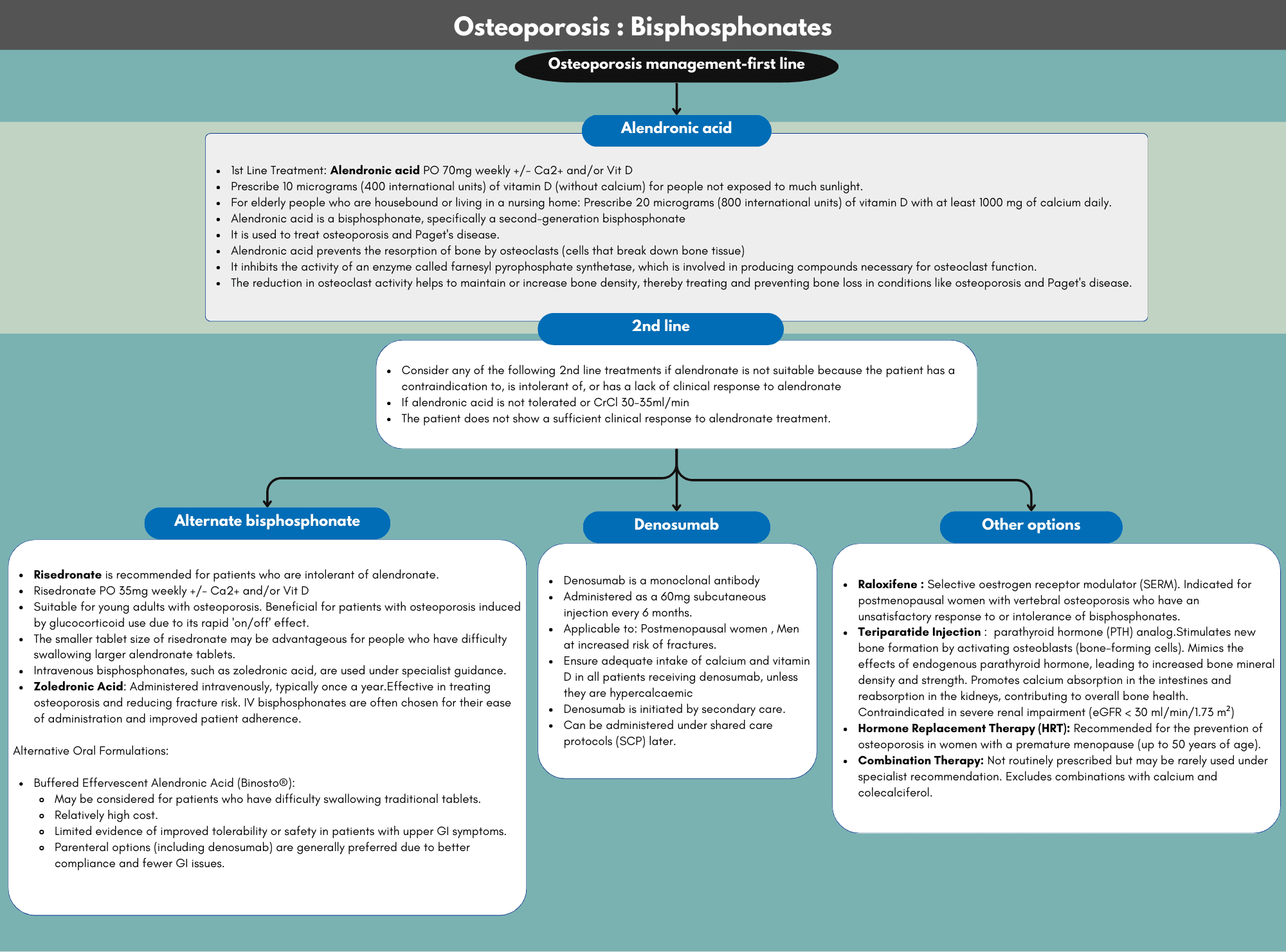
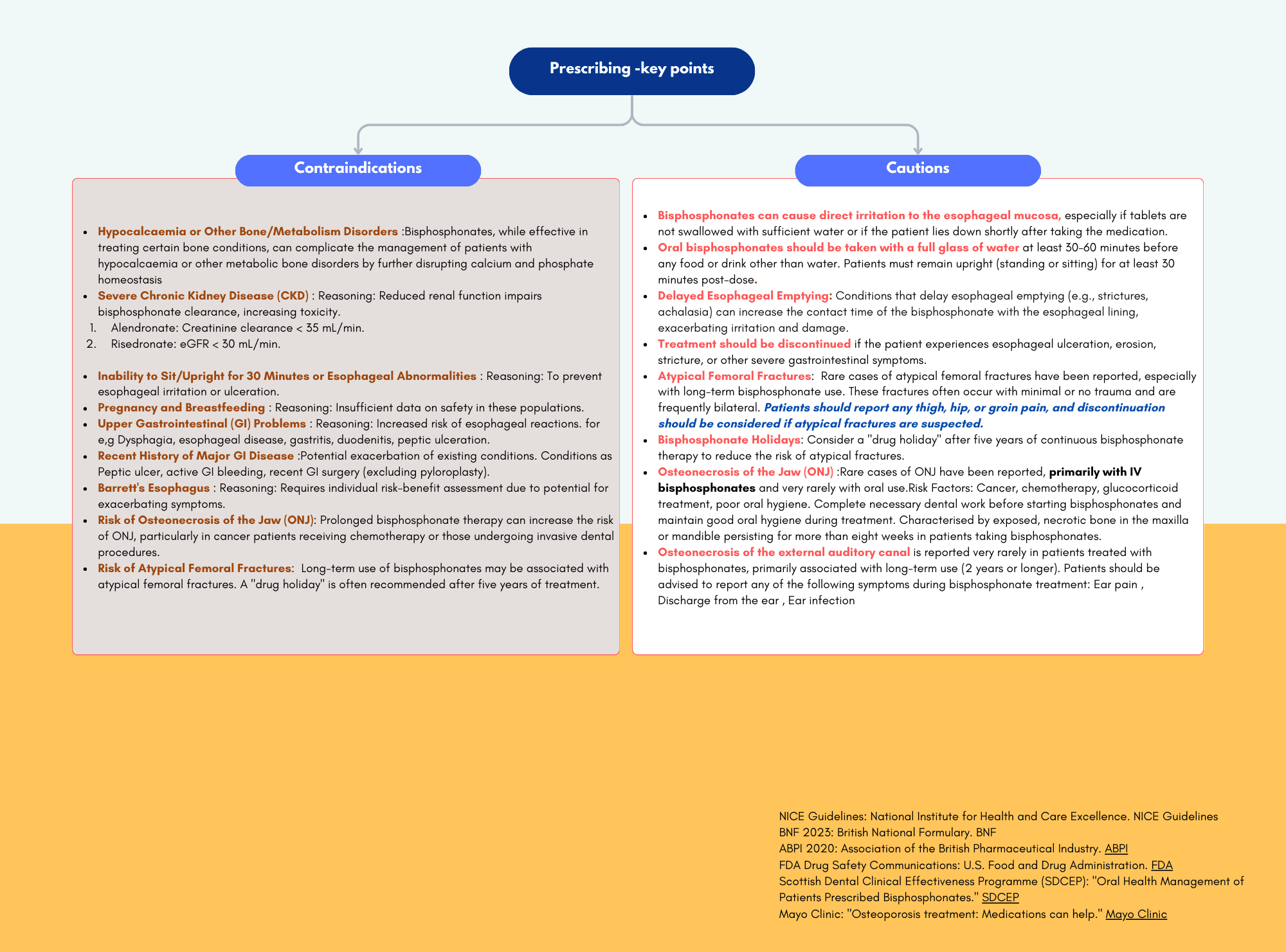
Bisphosphonates are a cornerstone in the management and treatment of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
These medications work by inhibiting bone resorption, thereby improving bone density and reducing the likelihood of fractures, particularly in postmenopausal women and individuals with a high risk of osteoporosis-related fractures. Commonly prescribed bisphosphonates include alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, and zoledronic acid. Understanding the indications, dosing regimens, side effects, and long-term efficacy of bisphosphonates is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes in osteoporosis management. Explore our comprehensive chart for a detailed comparison of these agents, including their specific uses, benefits, and potential adverse effects.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibition of Bone Resorption: Bisphosphonates bind to hydroxyapatite in bone, inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption, leading to increased bone density and reduced fracture risk. |
| First-Line Options | Oral Bisphosphonates: Alendronic acid, risedronate sodium, and ibandronic acid are common first-line choices for their efficacy in reducing vertebral and non-vertebral fractures. Intravenous Bisphosphonates: Zoledronic acid is preferred for patients who cannot tolerate oral bisphosphonates, have gastrointestinal contraindications, or have adherence issues. |
| Cost Considerations | Economic Factors: Choose the least expensive bisphosphonate option that aligns with the patient’s needs, considering the cost of the drug,... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.