Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
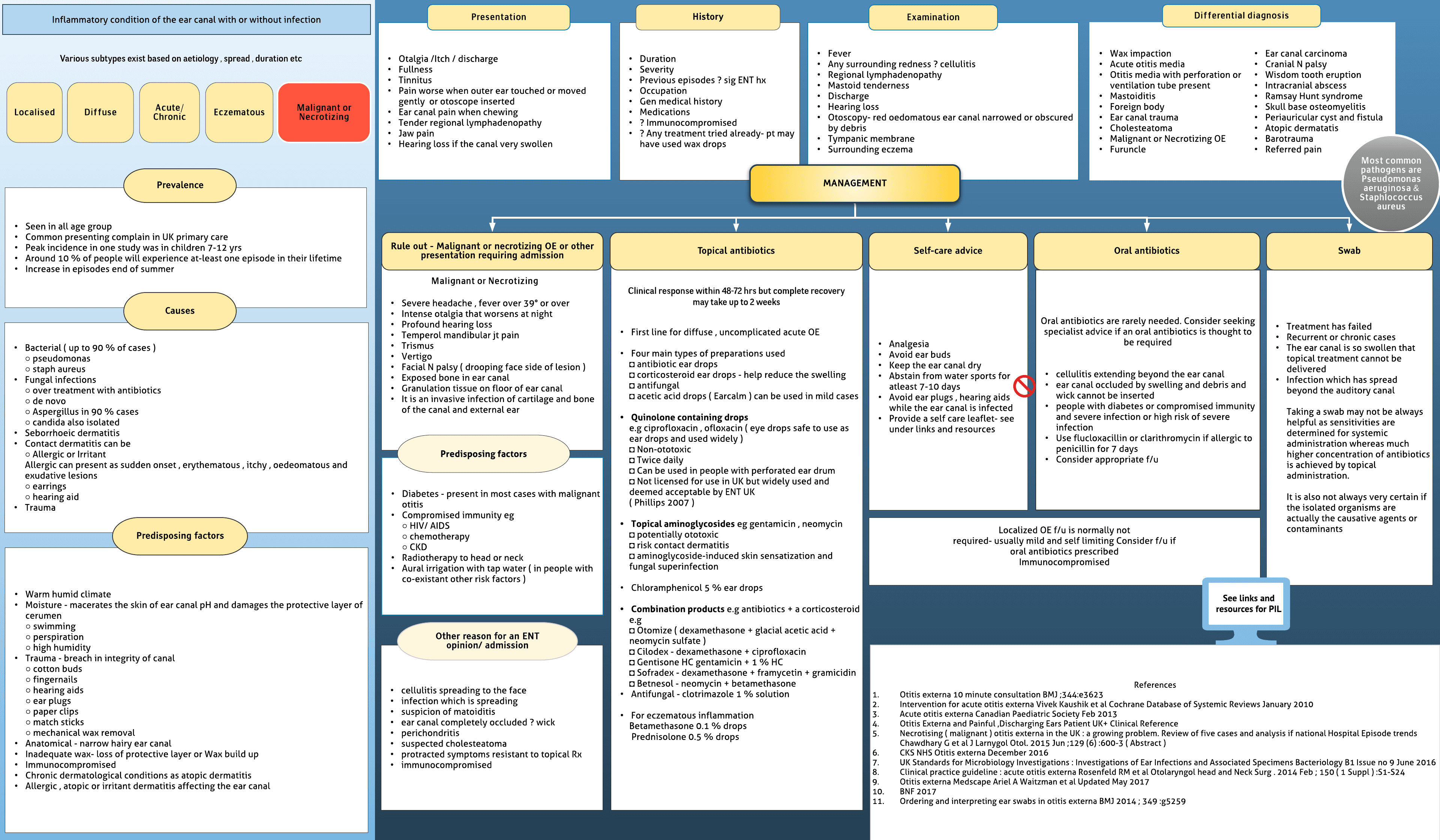
otitisOuter ear infection or otitis externa is frequently seen in Primary Care. This review of otitis externa on A4Medicine here is to make the reader aware of other conditions which can present similarly- Differential diagnosis and particular focus area on malignant or the necrotizing type ( osteomyelitis of the temporal bone ). Complexity in interpreting ear swab results is discussed. Treatment options are mentioned with a focus on topical treatment.
Inflammatory condition of the ear canal with or without infection Seen in all age group Common presenting complain in UK primary care Peak incidence in one study was in children 7-12 yrs Around 10 % of people will experience at-least one episode in their lifetime Increase in episodes end of summer
It can be difficult to distinguish OE from otitis media with discharge- if canal has discharge and swelling and TM cannot be seenTopical antibiotics are also Rx of choice for AOM with discharge and acute typmanostomy tube otorrhoea
Predisposing factors -Warm humid climate Moisture - macerates the skin of ear canal pH and damages the protective layer of cerumen○ swimming○ perspiration○ high humidity Trauma - breach in integrity of canal○ cotton buds○ fingernails○ hearing aids○ ear plugs○ paper clips○...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.