Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
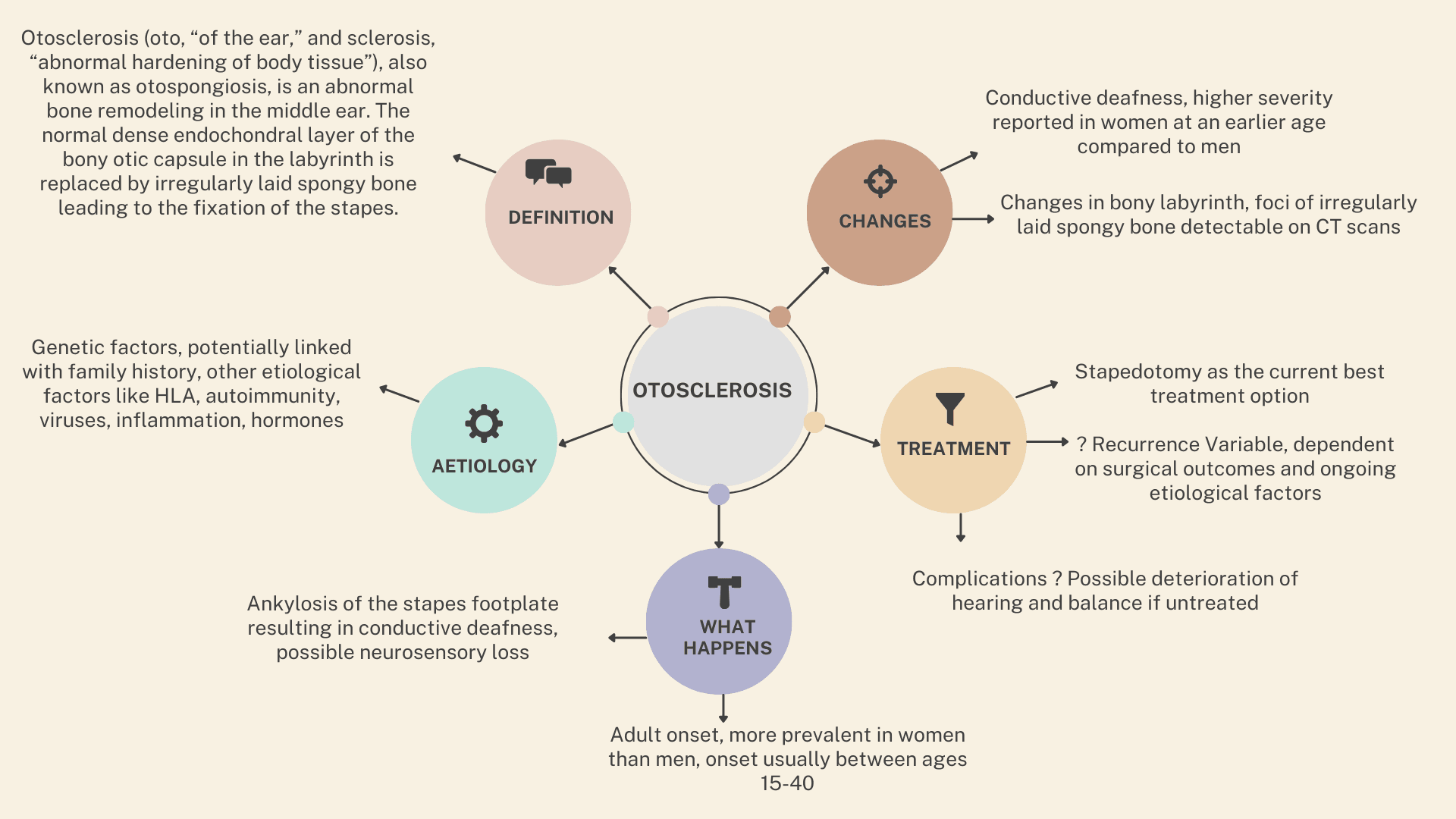
Otosclerosis is a complex pathological condition that predominantly affects the middle ear and is characterized by abnormal bone remodelling. The disease is of particular interest to clinicians as it is a leading cause of conductive hearing loss in adults. Understanding the nuances of otosclerosis, from its pathophysiology to its management, is crucial for primary care providers and specialists alike. The table below aims to encapsulate key aspects of otosclerosis, providing a quick reference. This includes its definition, epidemiology, symptoms, diagnostic tools, and current best practices for management.
| Criteria | Otosclerosis |
|---|---|
| Definition | Otosclerosis (oto, “of the ear,” and sclerosis, “abnormal hardening of body tissue”), also known as otospongiosis, is an abnormal bone remodeling in the middle ear. The normal dense endochondral layer of the bony otic capsule in the labyrinth is replaced by irregularly laid spongy bone leading to the fixation of the stapes. |
| Synonyms | Otospongiosis |
| Aetiology | Genetic factors, potentially linked with family history, other etiological factors like HLA, autoimmunity, viruses, inflammation, hormones |
| Clinical Presentation | Ankylosis of the stapes footplate resulting in conductive deafness, possible neurosensory loss |
| Demographics | Adult onset, more prevalent in women than men, onset usually between ages 15-40 |
| Symptoms | Conductive deafness, higher severity reported in women at an earlier... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.