Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
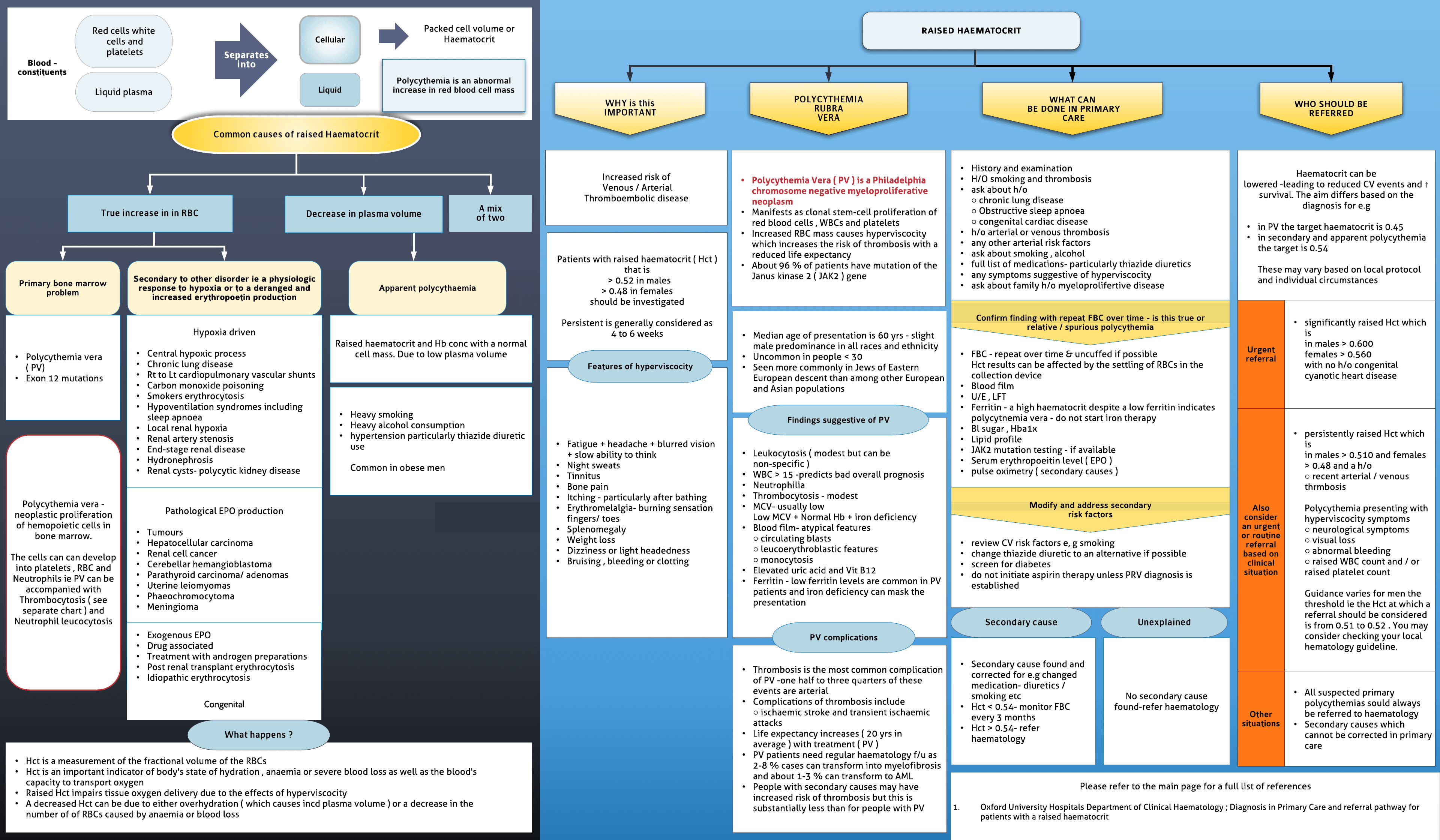
Polycythemia is an abnormal increase in red blood cell mass. Causes of polycythemia include a true increase in RBCs -Primary bone marrow problem or Secondary to other disorder ie a physiologic response to hypoxia or to a deranged and increased erythropoetin production.
Primary bone marrow problem -Polycythemia vera ( PV) Exon 12 mutations.
Secondary to other disorder ie a physiologic response to hypoxia or to a deranged and increased erythropoetin production -Hypoxia driven Central hypoxic process Chronic lung disease Rt to Lt cardiopulmonary vascular shunts Carbon monoxide poisoning Smokers erythrocytosis Hypoventilation syndromes including sleep apnoea Local renal hypoxia Renal artery stenosis End-stage renal disease Hydronephrosis Renal cysts- polycytic kidney disease.
Pathological EPO production Tumours Hepatocellular carcinoma Renal cell cancer Cerebellar hemangioblastoma Parathyroid carcinoma/ adenomas Uterine leiomyomas Phaeochromocytoma Meningioma.
Exogenous EPO Drug associated Treatment with androgen preparations Post renal transplant erythrocytosis Idiopathic erythrocytosis.
A decrease in plasma volume -Apparent polycythaemia-Raised haematocrit and Hb conc with a normal cell mass. Due to low plasma volume. Heavy smoking Heavy alcohol consumption hypertension particularly thiazide diuretic use Common in obese men.
What happens -Hct is a measurement of the fractional volume of the RBCs Hct is an important indicator of body's state of hydration...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.