Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
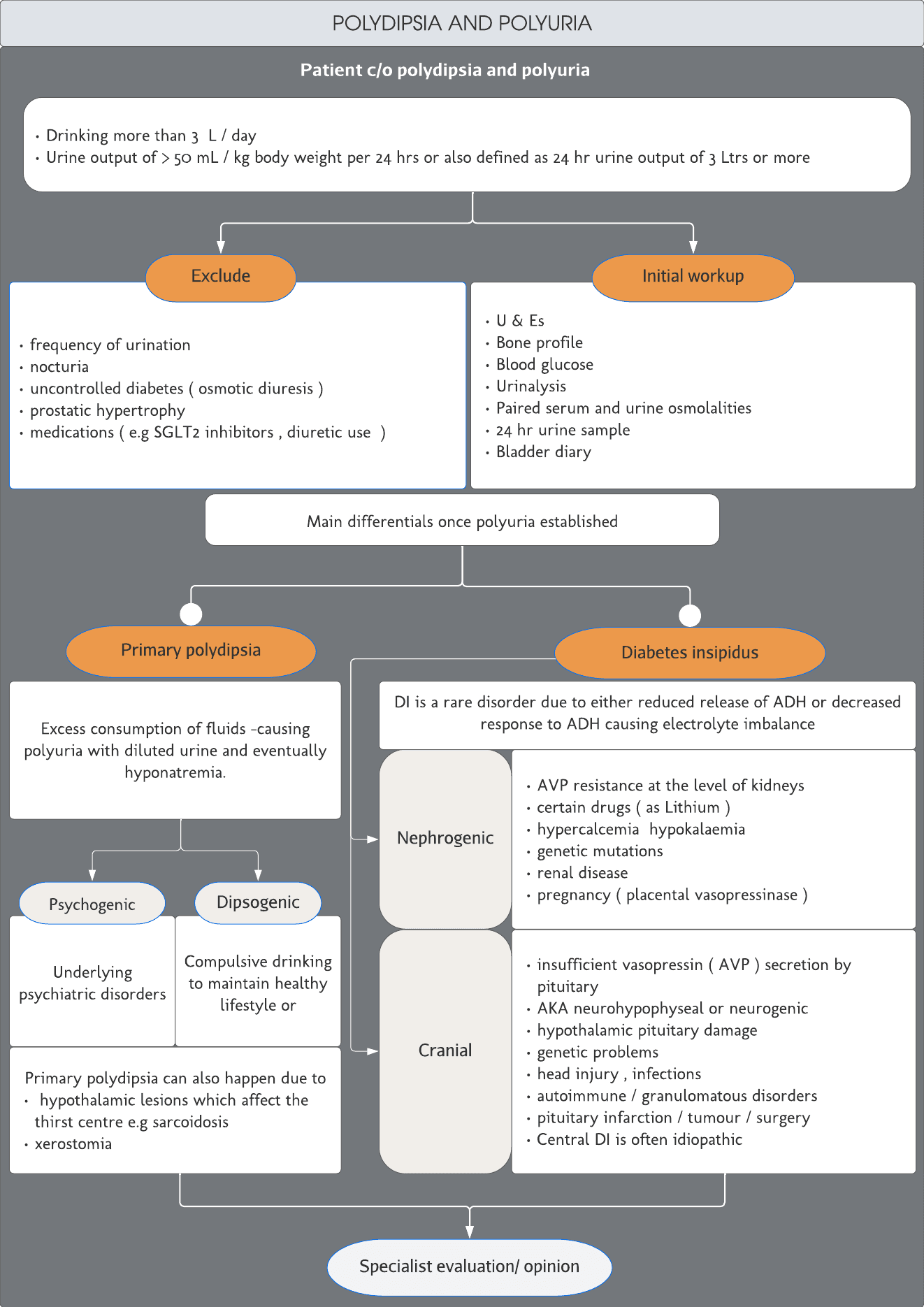
Drinking more than 3 L / day Urine output of > 50 mL / kg body weight per 24 hrs or also defined as 24 hr urine output of 3 Ltrs or more. frequency of urination nocturia uncontrolled diabetes ( osmotic diuresis ) prostatic hypertrophy medications ( e.g SGLT2 inhibitors , diuretic use ) U & Es Bone profile Blood glucose Urinalysis Paired serum and urine osmolalities 24 hr urine sample Bladder diary. Main differentials once polyuria established.
Primary poydipsia -Excess consumption of fluids -causing polyuria with diluted urine and eventually hyponatremia.
Diabetes inspidus -DI is a rare disorder due to either reduced release of ADH or decreased response to ADH causing electrolyte imbalance.
Nephrogenic -AVP resistance at the level of kidneys certain drugs ( as Lithium ) hypercalcemia hypokalaemia genetic mutations renal disease pregnancy ( placental vasopressinase )
Cranial- insufficient vasopressin ( AVP ) secretion by pituitary AKA neurohypophyseal or neurogenic hypothalamic pituitary damage genetic problems head injury , infections autoimmune / granulomatous disorders pituitary infarction / tumour / surgery Central DI is often idiopathic.
REFERENCES
Polyuria and Polydipsia Syndrome: is it Diabetes Insipidus? Prof Tricia Tan Consultant in Metabolic Medicine & Endocrinology Clinical Chemistry https://www.imperial.nhs.uk/-/media/website/gps-and-referrers/gp-documents/gp-professional-development/pathology-gp-study-afternoon-thursday-21-april-2016/tricia-tan---polyuria-and-polydipsia-gp-training-day-21st-april-2016-pptx.pdf?rev=f735ecc60a9347299d6b4213fbf337fd&hash=2801B370B24CEA8ED4F7C52890135A3A
New diagnostic approaches...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.