Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
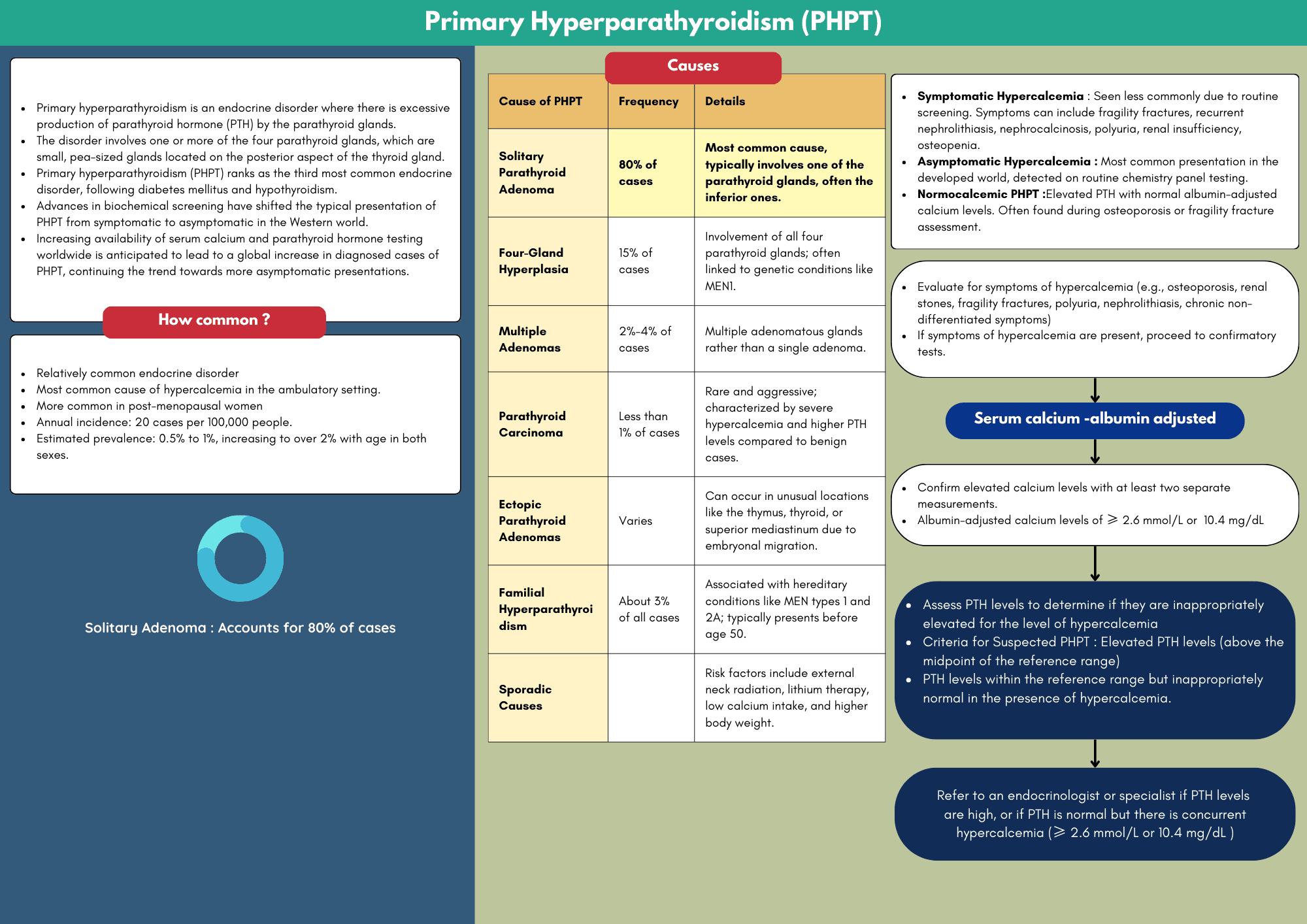
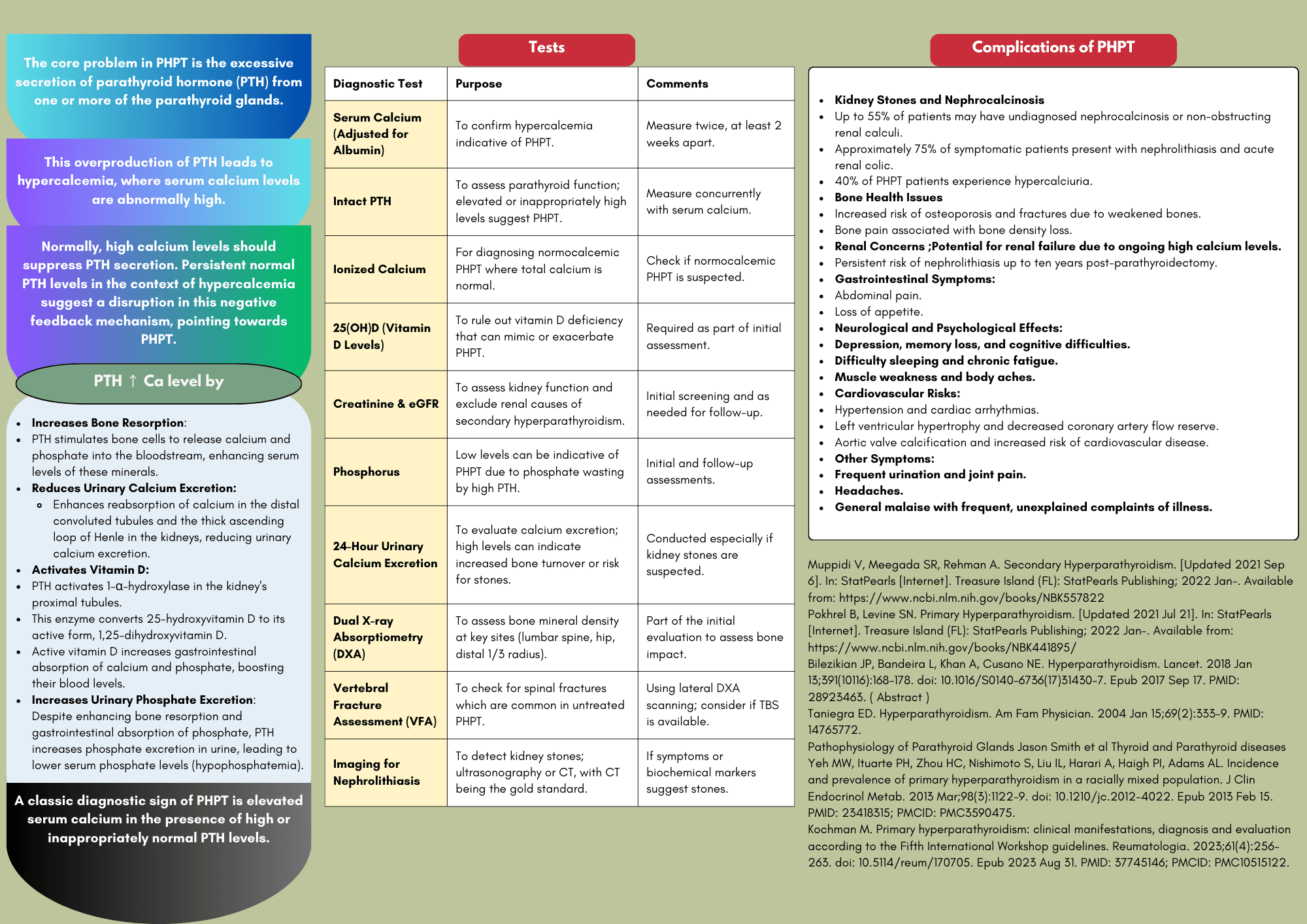
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is a common endocrine disorder characterized by the overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH), leading to elevated serum calcium levels (hypercalcemia). It is most frequently caused by a single-gland adenoma, particularly in middle-aged women, but can also arise from hyperplasia or carcinoma of the parathyroid glands.
Parathyroid hyperplasia and, more rarely, parathyroid carcinoma (PTC) can also contribute to the development of PHPT. PTC is a rare malignancy, representing only 0.4% to 5.2% of all reported cases of hyperparathyroidism and approximately 0.2% to 0.5% of malignant endocrine tumors overall.
Clinically, patients may present with a variety of symptoms, including nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), musculoskeletal pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, and neuropsychiatric symptoms such as mood changes or cognitive impairment. However, hypercalcemia is often discovered incidentally during routine blood tests, making awareness of this condition crucial for primary care clinicians.
As the incidence of primary hyperparathyroidism increases with age, primary care clinicians play a crucial role in its early detection and management. Routine laboratory tests, including serum calcium and PTH levels, are essential for diagnosing PHPT, especially in patients presenting with nonspecific symptoms or those undergoing routine health screenings.
Recognizing the signs of hyperparathyroidism is vital, as untreated PHPT can lead to significant...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.