Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
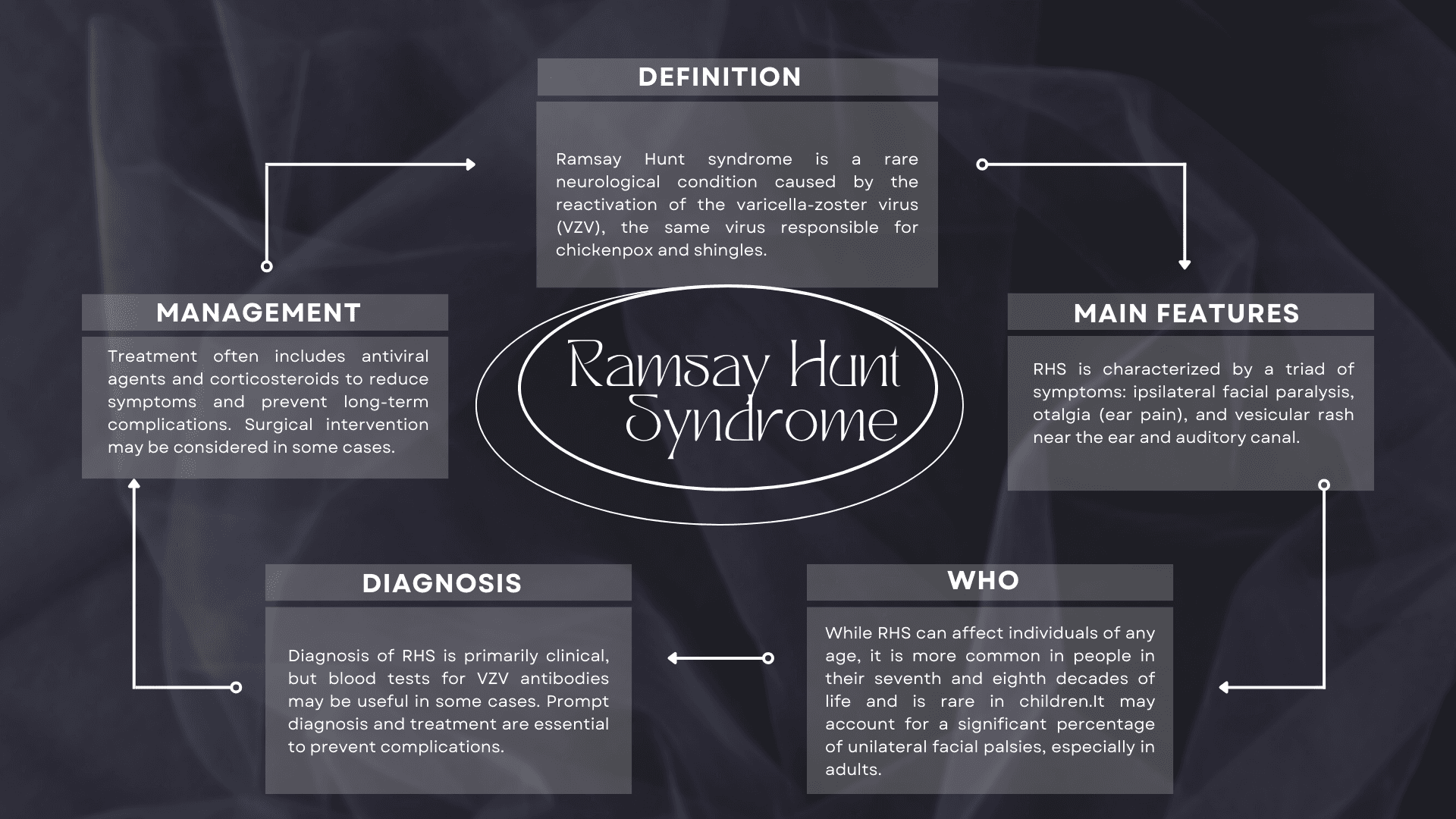
Ramsay Hunt syndrome (RHS), also known as herpes zoster oticus, is a distinct clinical entity characterized by a specific set of symptoms and complications resulting from varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection. This table provides a comprehensive overview of RHS, including its definition, incidence, pathogenesis, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications. Understanding the key features of RHS is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | ○ Ramsay Hunt syndrome (RHS), also known as herpes zoster oticus, is a late complication of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection, primarily affecting the geniculate ganglion of cranial nerve VII. ○ It is characterized by a clinical triad of ipsilateral facial paralysis, otalgia, and vesicles near the ear and auditory canal. |
| Incidence | • RHS is the second most common cause of non-traumatic facial palsy in adults. • Estimated to account for 16% of all causes of unilateral facial palsies in children and 18% in adults. • Thought to cause up to 20% of clinically diagnosed cases of Bell's Palsy. • About 7% of RHS cases result in acute facial paralysis. • Affects individuals of all ages but is more common in those in their seventh and eighth decades. • Rare in children. |
| Pathogenesis... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.