Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
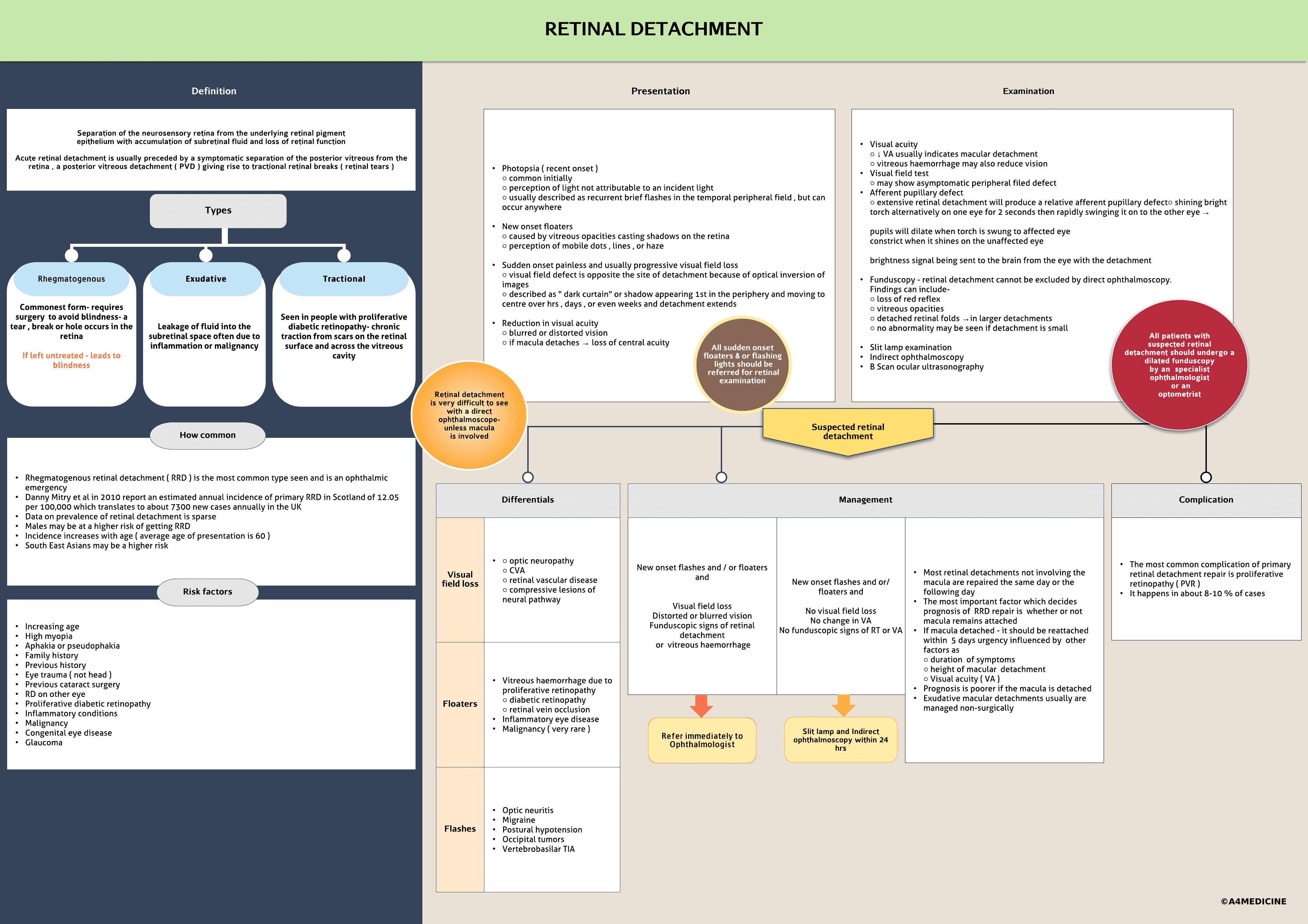
Separation of the neurosensory retina from the underlying retinal pigment epithelium with accumulation of subretinal fluid and loss of retinal functionAcute retinal detachment is usually preceded by a symptomatic separation of the posterior vitreous from the retina , a posterior vitreous detachment ( PVD ) giving rise to tractional retinal breaks ( retinal tears )Symptoms of PVD include light flashes and floaters and such patients are at high risk pf retinal detachment
Risk factors- Increasing age Myopia Family history Previous history Eye trauma ( not head ) Previous cataract surgery RD on other eye Proliferative diabetic retinopathy Inflammatory conditions Malignancy Congenital eye disease
Presentation- Photopsia ( recent onset ) ○ common initially○ perception of light not attributable to an incident light○ usually described as recurrent brief flashes in the temporal peripheral field , but can occur anywhere New onset floaters○ caused by vitreous opacities casting shadows on the retina○ perception of mobile dots , lines , or haze Sudden onset painless and usually progressive visual field loss○ visual field defect is opposite the site of detachment because of optical inversion of images○ described as " dark curtain" or shadow appearing 1st in the periphery and moving to centre over hrs...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.