Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
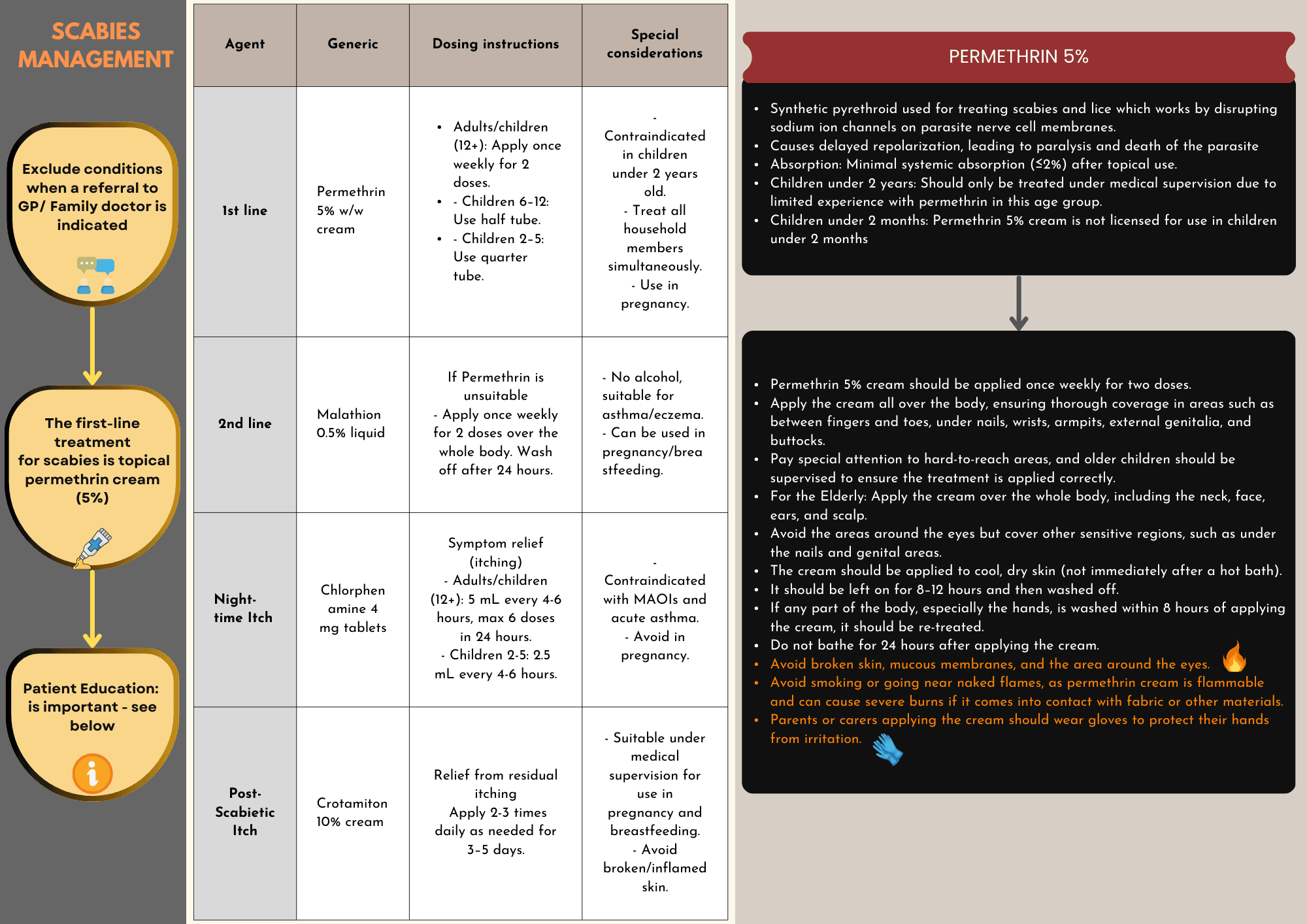
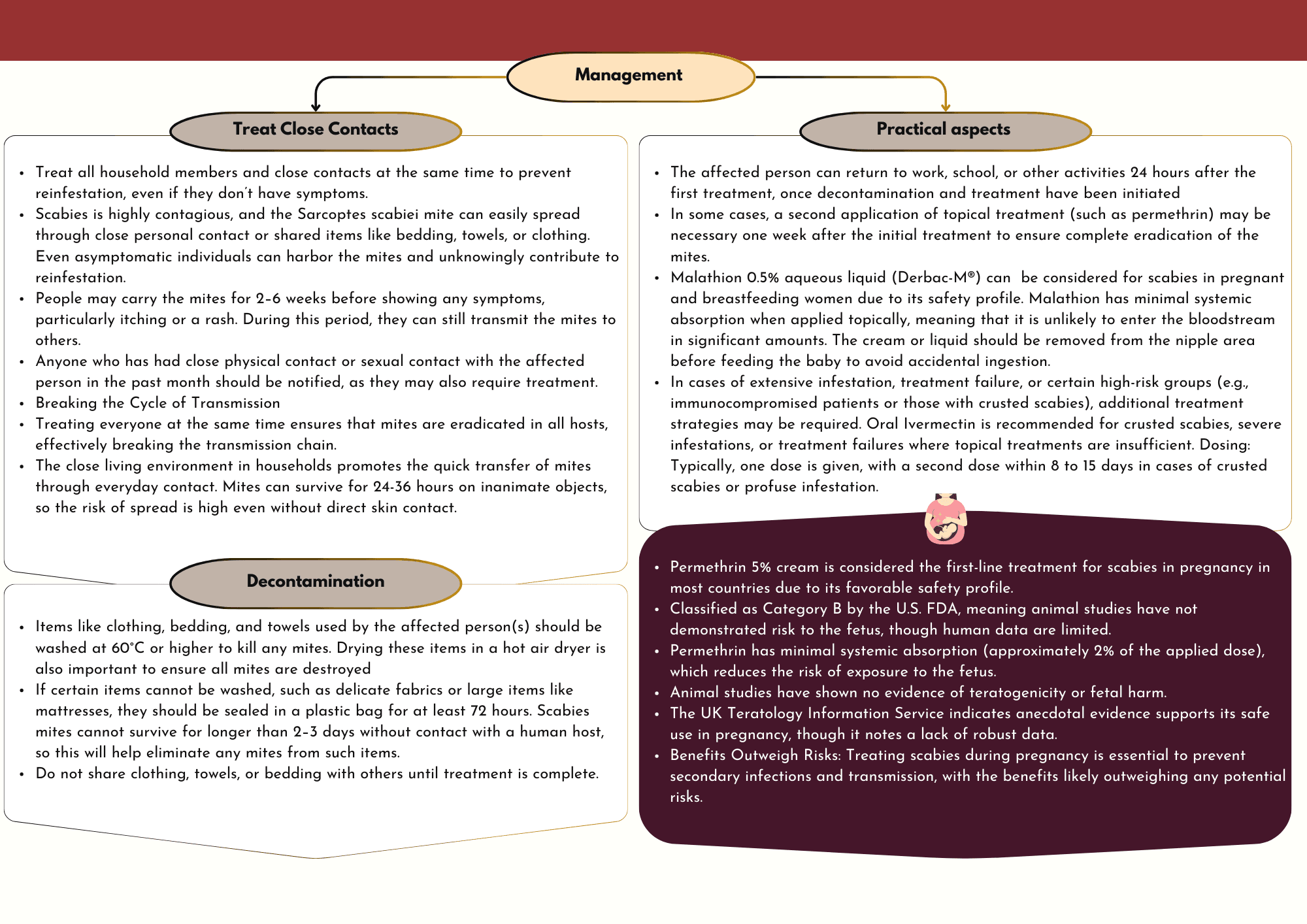
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. It presents with intense itching, especially at night, and a rash consisting of small, red bumps. Transmission occurs through close physical contact, making outbreaks common in households and institutions such as care homes.
Primary care professionals like nurses, pharmacists, and paramedics play a critical role in the management of scabies. Effective management involves timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures to limit the spread of infestation.
Diagnosis:
First-Line Treatment:
Simultaneous Treatment:
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.