Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
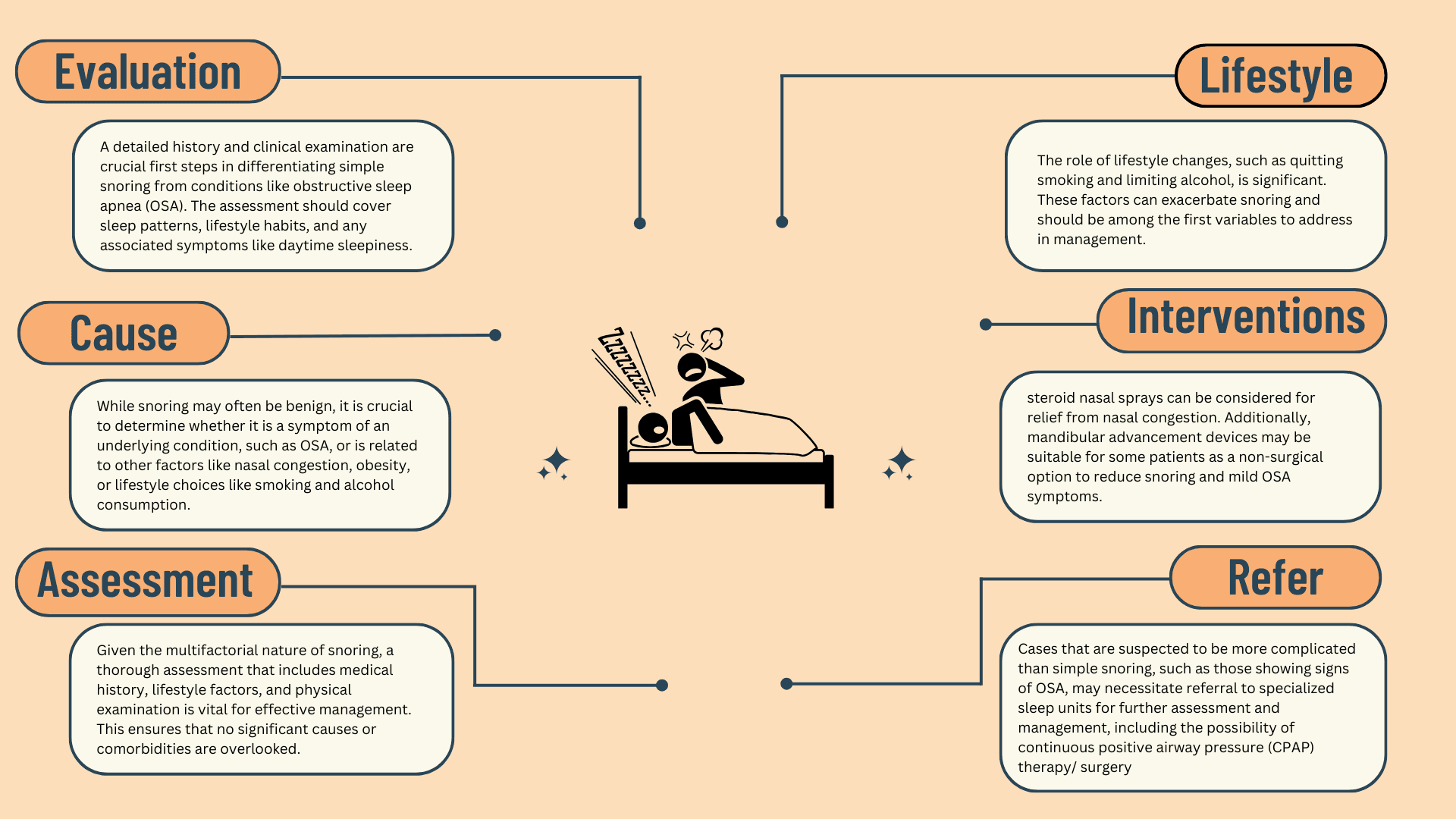
Snoring is a common clinical complaint encountered in primary care settings, affecting both the individual who snores and those who share their living environment. Characterized by a noisy breathing sound during sleep, snoring arises from the vibration of soft tissues in the upper airway. Although often considered benign, snoring can significantly disrupt sleep quality and may be a symptom of more serious underlying conditions, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
The clinical evaluation and management of snoring is a multi-faceted endeavour. It involves comprehensive history-taking to distinguish simple snoring from potentially severe conditions like OSA. Physical examination is vital to identify anatomical features that contribute to snoring and to evaluate associated comorbidities like obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Finally, the management of snoring involves an array of interventions ranging from lifestyle modifications to pharmacological treatments and surgical options.
The following tables aim to provide primary care clinicians with a structured approach for the evaluation and management of patients presenting with snoring. This includes questions for detailed history-taking, key physical examination points, and a broad spectrum of treatment options to consider.
| Section | Description and Criteria | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| What Happens: Pharyngeal Airway Dynamics | During sleep, the tone of the pharyngeal dilator muscles decreases, leading... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.