Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
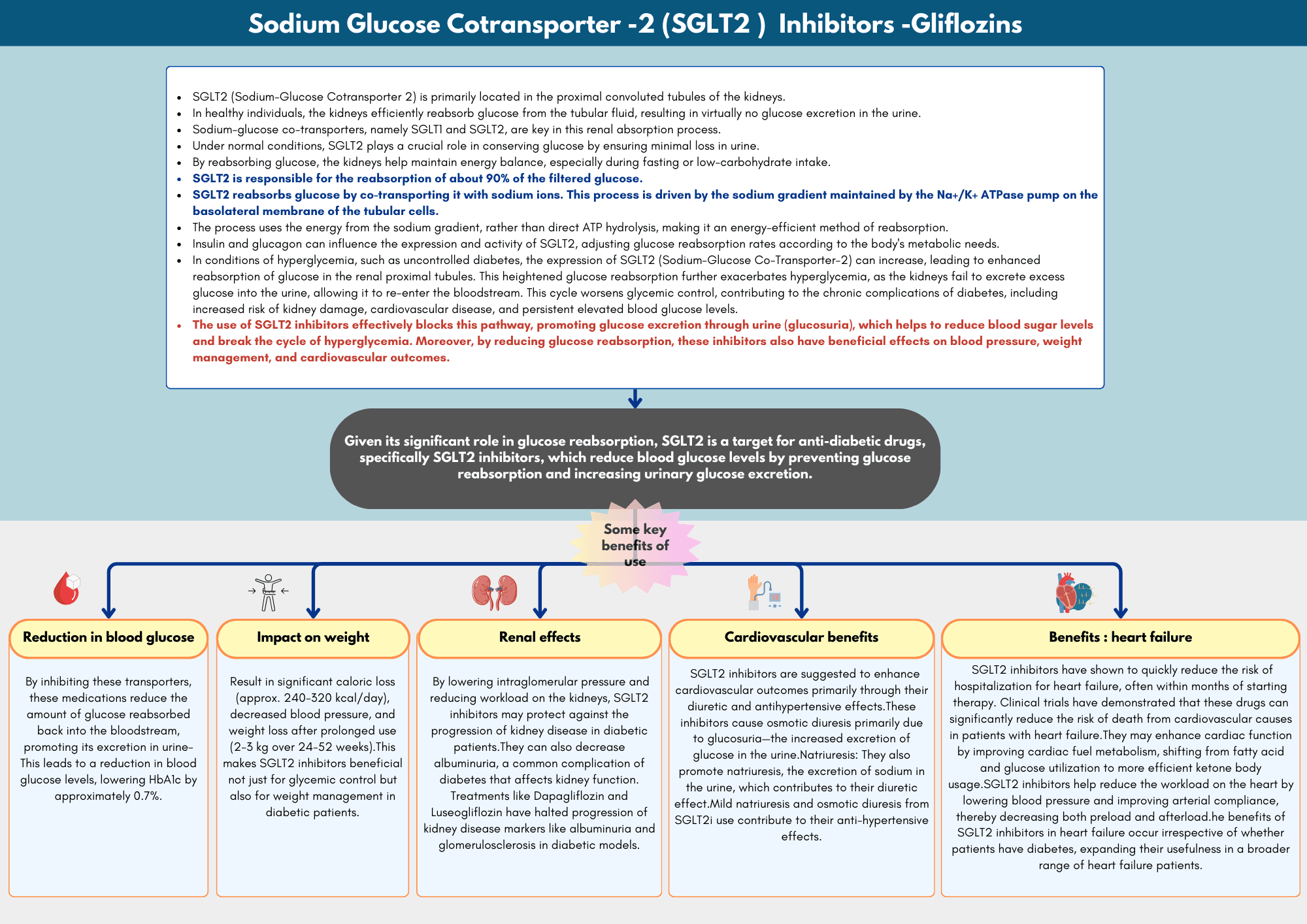
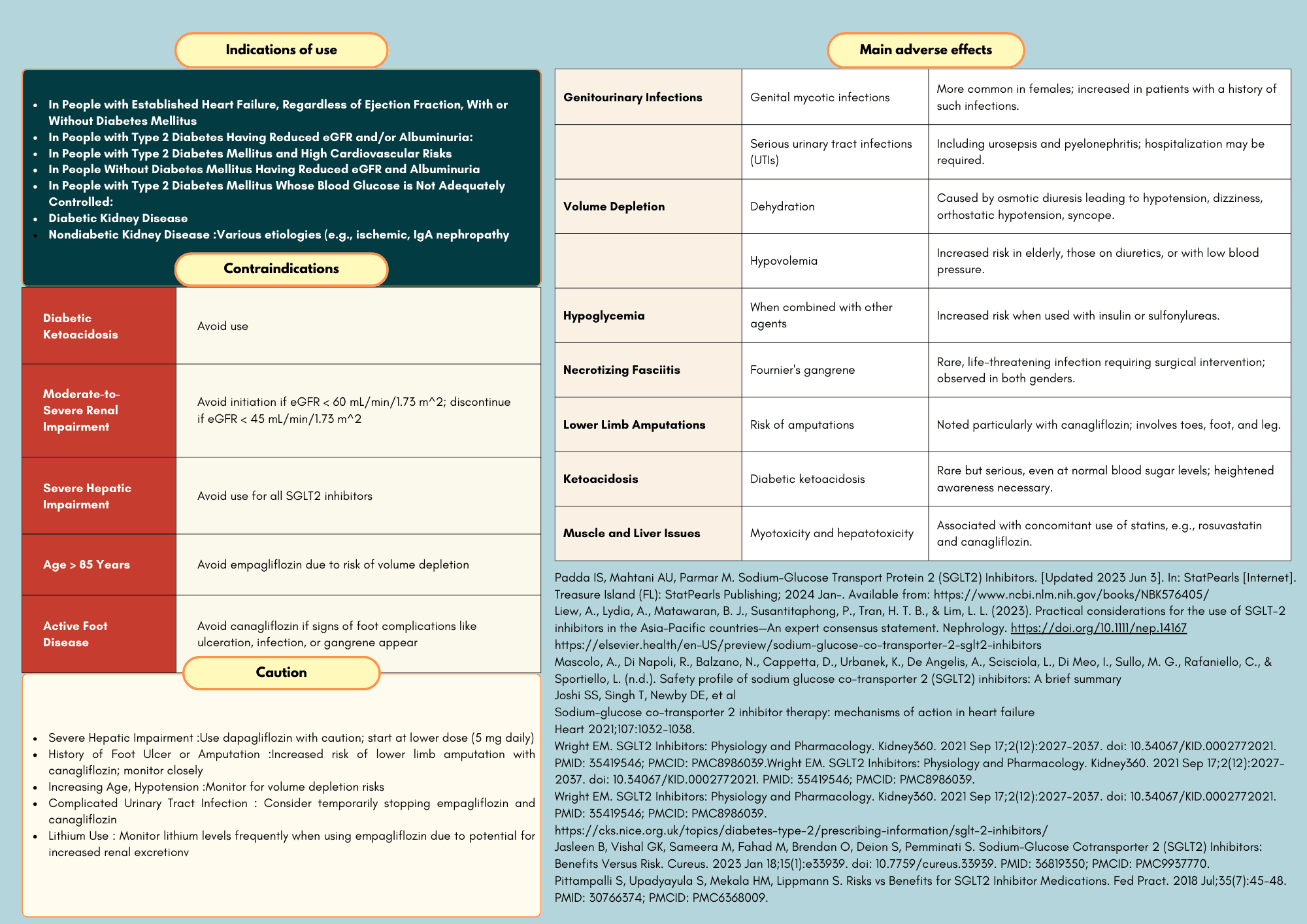
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2 inhibitors) are a class of medications that have gained widespread use in the management of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and are increasingly recognized for their benefits beyond glycaemic control. These drugs work by inhibiting the SGLT2 proteins in the renal proximal tubules, which are responsible for reabsorbing glucose back into the bloodstream. By blocking this pathway, SGLT2 inhibitors promote urinary glucose excretion, leading to lower blood glucose levels.
SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and canagliflozin, have been shown to reduce HbA1c, assist with weight loss, and lower blood pressure, making them valuable in addressing multiple aspects of metabolic syndrome. Beyond their role in glycaemic control, emerging evidence highlights their benefits in cardiovascular and renal protection, with notable reductions in hospitalizations for heart failure and slowing the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
SGLT2 inhibitors, including canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and ertugliflozin, have shown multiple benefits beyond glucose control, such as promoting weight loss and improving cardiovascular outcomes, particularly in patients with diabetes who have existing cardiovascular disease or heart failure. These drugs reduce blood glucose levels by increasing urinary glucose excretion, but their effects on weight and cardiovascular health...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.