Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
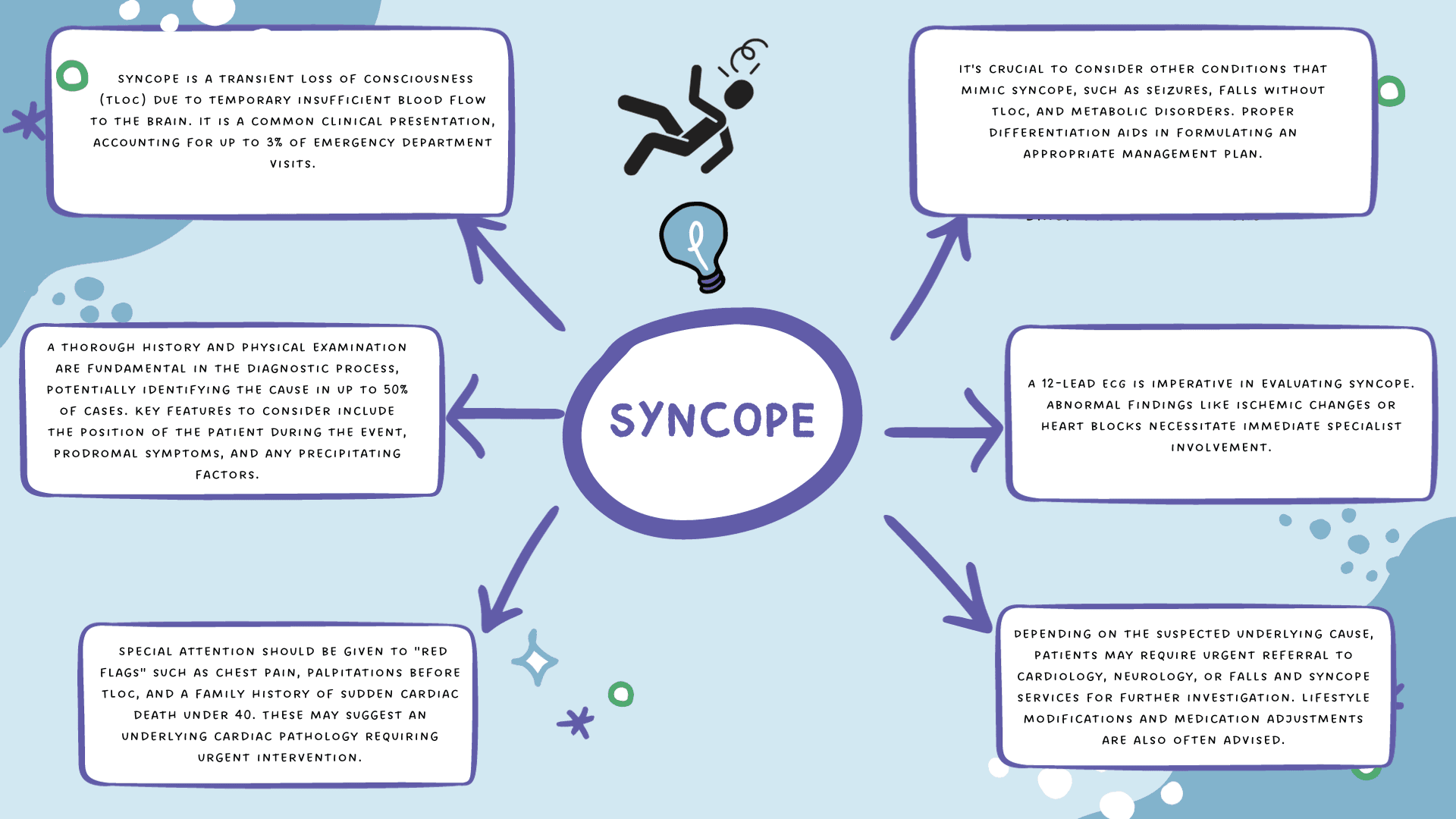
Syncope, commonly referred to as "fainting," is a temporary loss of consciousness (TLoC) characterized by a rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous complete recovery. It is a prevalent condition with a broad differential diagnosis that encompasses benign to life-threatening etiologies. The phenomenon occurs due to transient cerebral hypoperfusion, which may arise from various underlying mechanisms such as reflex triggers, cardiac conditions, and orthostatic changes. Accurate diagnosis and management are critical, as the implications of misdiagnosis can be severe.
In primary care settings, clinicians frequently encounter patients presenting with syncope or blackout episodes. The challenge lies in identifying the underlying cause, which often requires a nuanced approach combining history-taking, physical examination, and appropriate investigations. Immediate referral to emergency services or specialized care is mandated in cases where life-threatening conditions are suspected. Equally crucial is patient education and lifestyle advice, especially when dealing with recurrent or less severe cases of syncope.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Syncope is a sudden, transient loss of consciousness (TLOC) due to cerebral hypoperfusion. It is characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. |
| Duration | The average duration is approximately 12 seconds. |
| Recovery | Immediate and spontaneous recovery without the need for electrical or chemical cardioversion. |
| Posture | Inability to... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.