Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
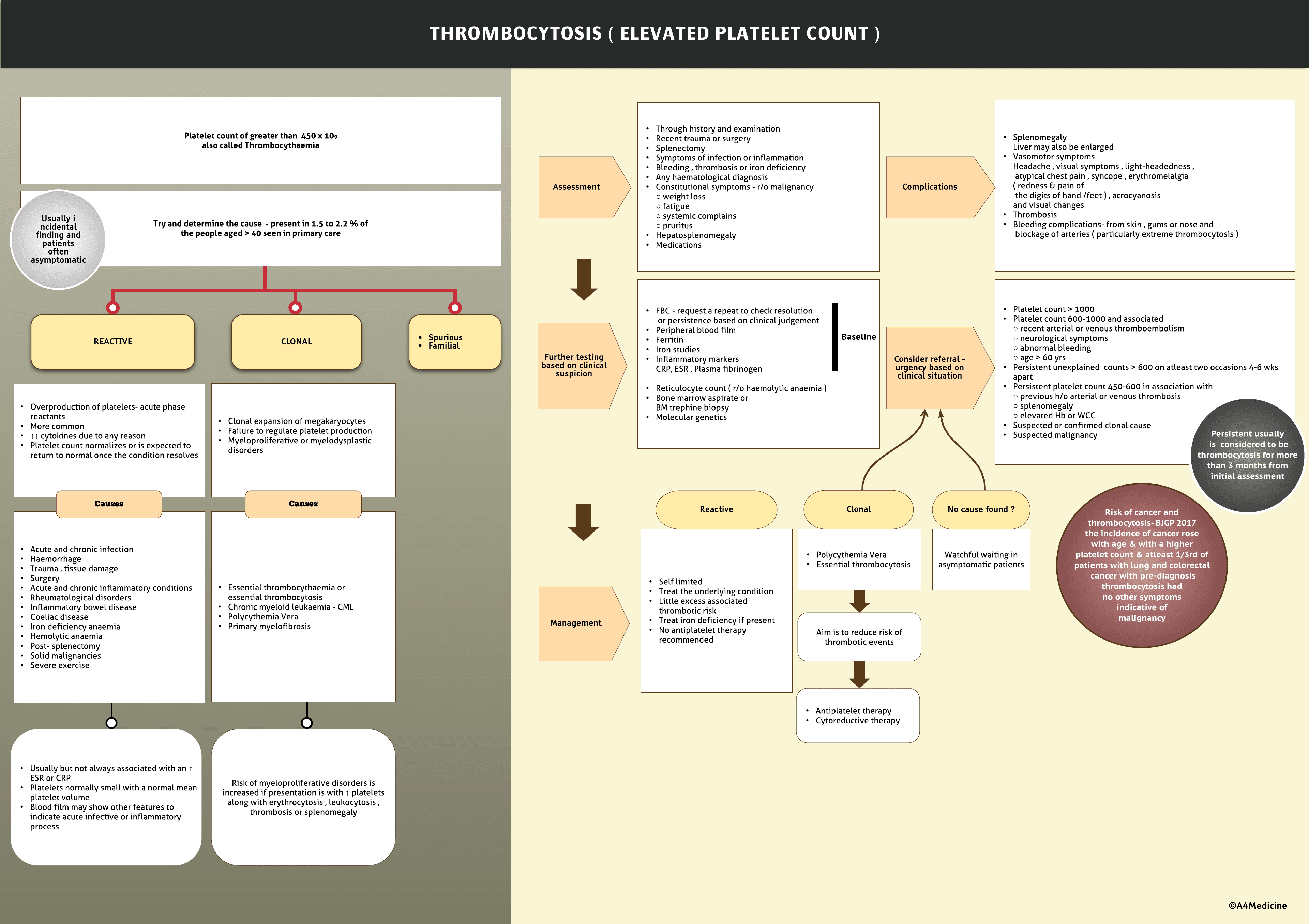
Thrombocytosis or raised -Platelet count of greater than 450 x 109 also called Thrombocythaemia
Try and determine the cause - present in 1.5 to 2.2 % of the people aged > 40 seen in primary care REACTIVE-Overproduction of platelets- acute phase reactants More common ↑↑ cytokines due to any reason Platelet count normalizes or is expected to return to normal once the condition resolves Acute and chronic infection Haemorrhage Trauma , tissue damage Surgery Acute and chronic inflammatory conditions Rheumatological disorders Inflammatory bowel disease Coeliac disease Iron deficiency anaemia Hemolytic anaemia Post- splenectomy Solid malignancies Severe exercise Usually but not always associated with an ↑ ESR or CRP Platelets normally small with a normal mean platelet volume Blood film may show other features to indicate acute infective or inflammatory process
CLONAL-Clonal expansion of megakaryocytes Failure to regulate platelet production Myeloproloferative or myelodysplastic disorders Essential thrombocythaemia or essential thrombocytosis Chronic myeloid leukaemia - CML Polycythemia vera Primary myelofibrosis
Risk of myeloproliferative disorders is increased if presentation is with ↑ platelets along with erythrocytosis , leukocytosis , thrombosis or splenomegaly
history-Recent trauma or surgery Splenectomy Symptoms of infection or inflammation Bleeding , thrombosis or iron deficiency Any haematological diagnosis Constitutional symptoms -...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.