Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
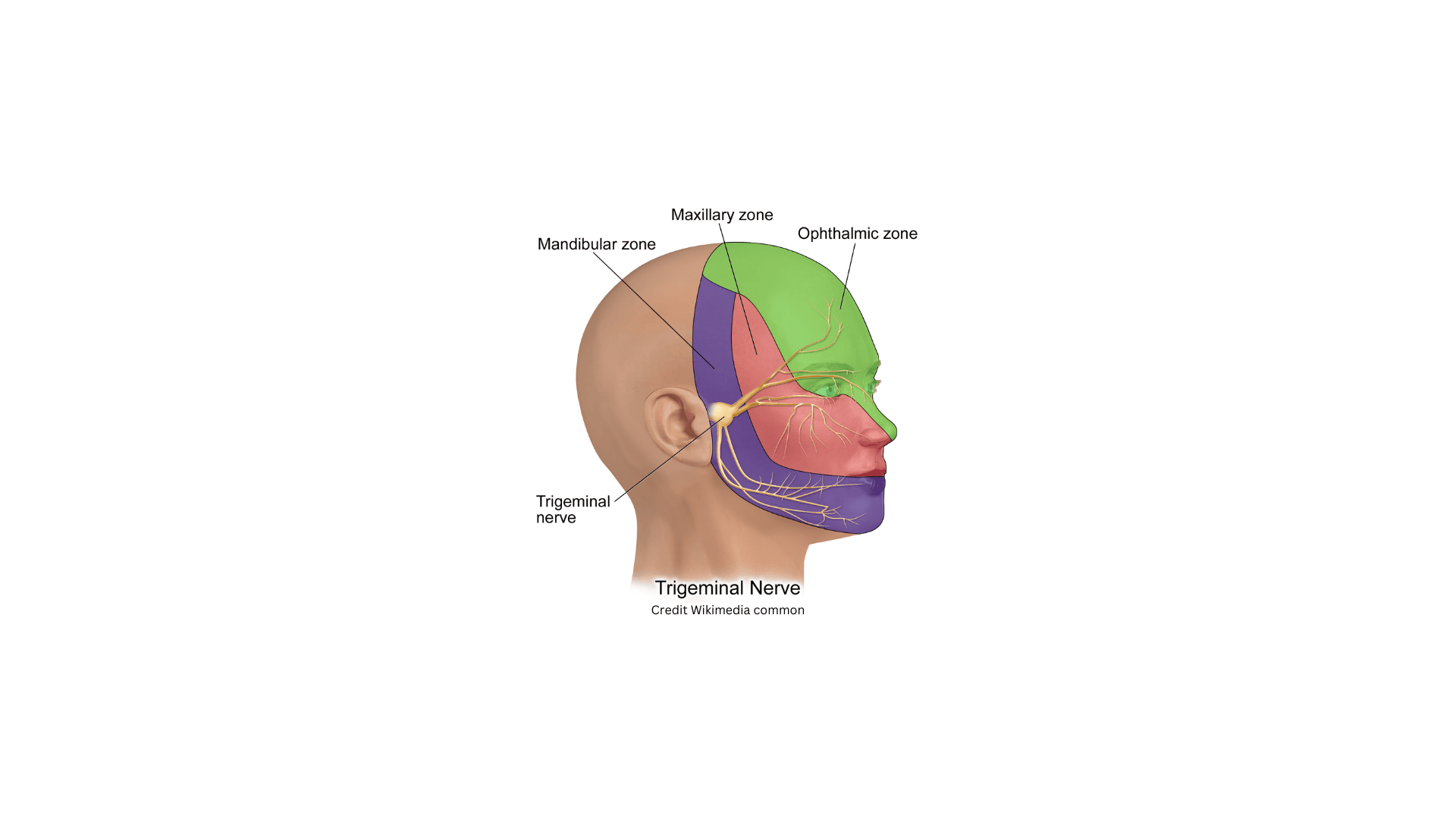
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Nerve Name | Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) |
| Divisions | • Ophthalmic (V1) • Maxillary (V2) • Mandibular (V3) |
| Sensory Functions | • V1: Cornea, ciliary body, lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, and parts of the nasal cavity. • V2: Maxillary teeth, nasal cavity, palate, nasopharynx, maxillary, and ethmoid sinuses. • V3: Mandibular teeth, anterior two-thirds of the tongue, mucosa of the cheek, and temporal region. |
| Motor Functions | Innervates muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini. |
| Nuclei | • Mesencephalic nucleus • Principal sensory nucleus • Spinal nucleus |
| Foramen | • V1: Superior orbital fissure • V2: Foramen rotundum • V3: Foramen ovale |
| Pathophysiology in Neuralgia | ♦ Compression or irritation of nerve roots, typically at the entry zone into the pons, can cause trigeminal neuralgia. ♦ Vascular compression by the superior cerebellar artery is the most common cause. |
| Clinical Implications | - Sensory loss or tingling in the distribution of one or more branches can indicate nerve damage. - Hyperactivity of the nerve can lead to severe pain episodes characteristic of trigeminal neuralgia. |
Introduction and epidemiology
| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| Definition | Trigeminal Neuralgia is characterized by recurrent, unilateral, brief, intense electric... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.