Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
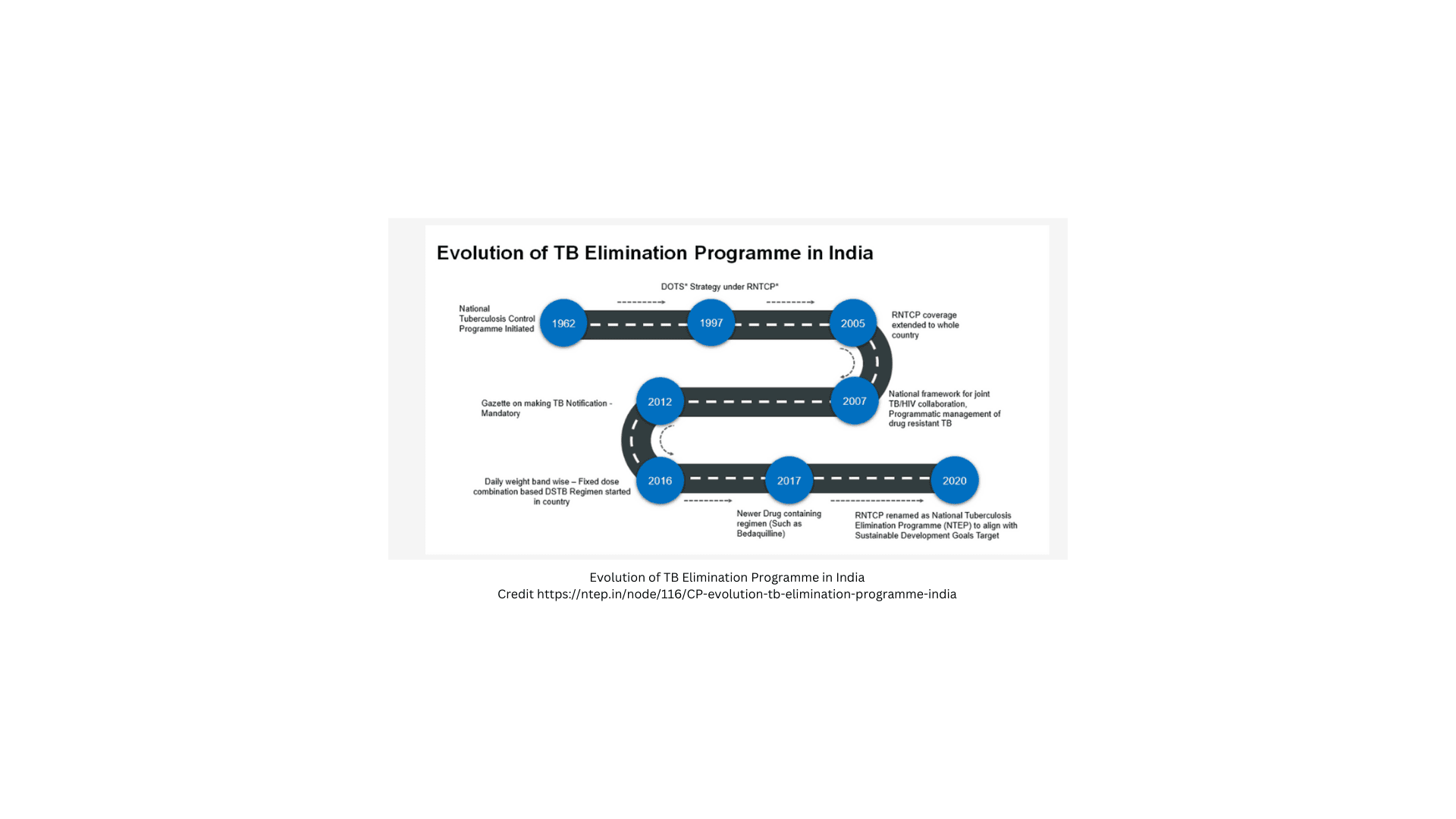
Tuberculosis (TB), a formidable public health challenge, remains one of the deadliest diseases globally, responsible for significant mortality and morbidity. Despite over 50 years of TB control efforts in India, the country continues to face a high burden of the disease, with an estimated 480,000 deaths annually and numerous cases that go undiagnosed or inadequately treated. The World Health Assembly's End TB Strategy, aimed at eradicating the global TB epidemic by 2035, highlights the need for integrated, patient-centered care and prevention, underlining a paradigm shift in the global approach to tackling TB. This goal aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), calling for intensified actions across various sectors, including health, socioeconomic interventions, and research.
India's National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination reflects a commitment to drastically reduce the incidence and mortality of TB. Building on the accomplishments and learnings of the previous NSP (2012–2017), which saw improvements in diagnostics, treatment, and program integration, the NSP 2017–2025 proposes bold and innovative steps towards eliminating TB. This plan involves comprehensive strategies, including mandatory case notification, expansion of diagnostic services, and effective management of drug-resistant TB and TB-HIV co-infections. The plan also recognizes the setbacks experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic and the...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.