Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
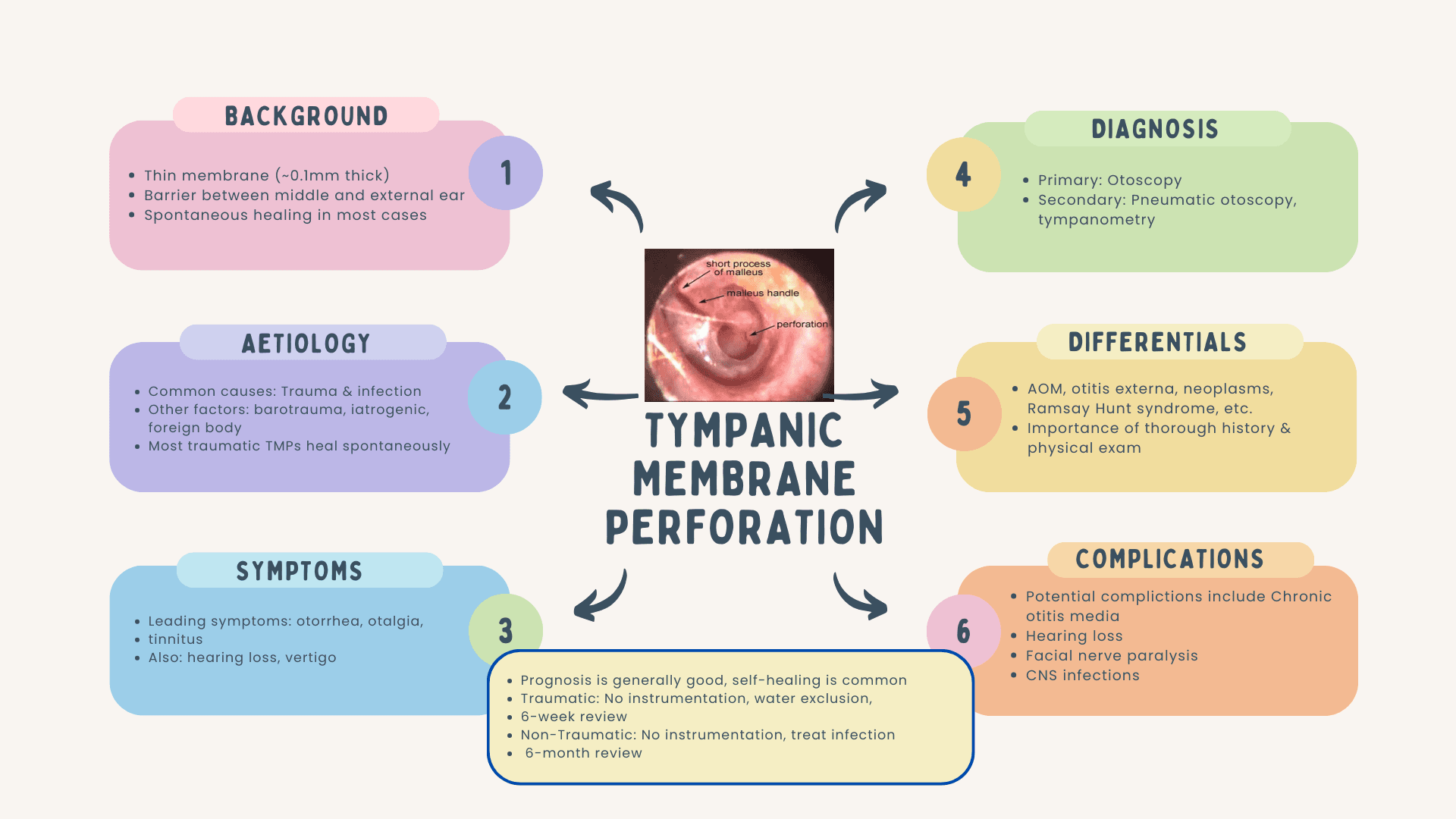
The following table provides a brief guide to Tympanic Membrane Perforation (TMP), a common clinical issue encountered in primary care settings. This table aims to be a quick yet thorough resource for clinicians. It covers essential topics from the anatomy and function of the tympanic membrane to the clinical presentation, diagnostic approaches, and differential diagnoses related to TMP. Each section is meticulously researched and cited to offer a comprehensive understanding of this condition. The information is designed to assist primary care clinicians in the prompt and accurate diagnosis, management, and when necessary, referral of cases involving tympanic membrane perforation.
| Section | Information |
|---|---|
| Definition and Background | ♦ The tympanic membrane is a thin, semitransparent structure approximately 0.1 mm thick and 10-11 mm long ♦ Serves as a barrier between the external auditory canal and the middle ear, essential for sound conduction ♦ TMP is defined as a partial or full tear in this membrane due to various causes like trauma, infection, tumours, or iatrogenic interventions ♦ While most TMPs heal spontaneously, around 10% become chronic [Downey et al., 2003]. |
| Aetiology | • Trauma and AOM are common causes. • Simple Traumatic TMP (TTMP) is the most prevalent form of trauma-induced otologic dysfunction |
| Symptoms... |
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.