Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
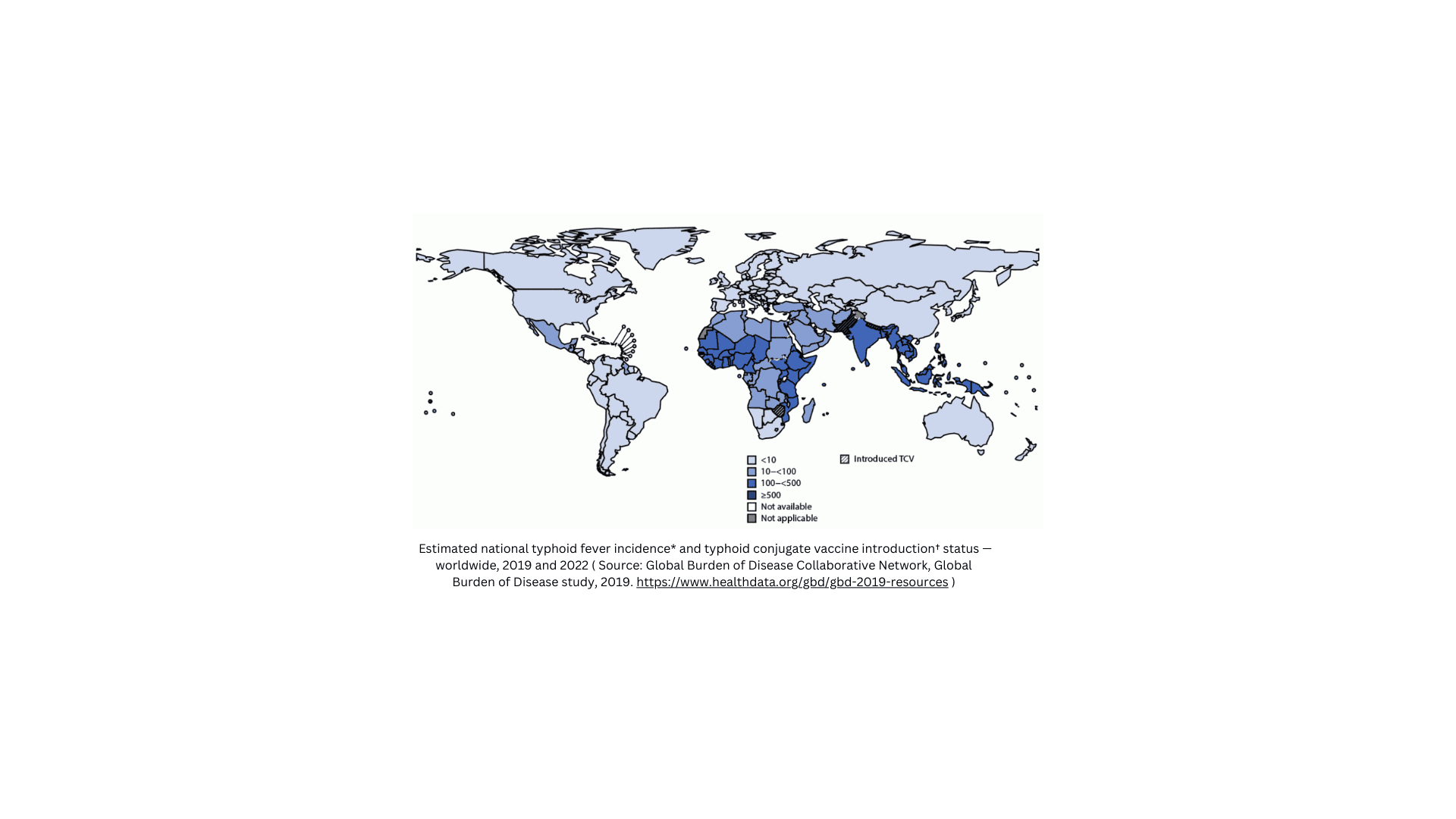
Typhoid fever, enteric fever, and paratyphoid are bacterial infections primarily affecting the intestinal system and occasionally the bloodstream. These conditions are significant public health concerns, especially in areas with inadequate sanitation and water supply. Understanding these terms is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies in healthcare.
| Term | Definition | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Typhoid Fever | A systemic infection caused primarily by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. | Characterized by fever, headache, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhoea. Often associated with poor sanitation and contaminated food or water. |
| Enteric Fever | A broader term that encompasses both typhoid and paratyphoid fever. It refers to a systemic illness caused by enteric pathogens. | Symptoms include high fever, gastrointestinal disturbances, and possible complications like intestinal haemorrhage or perforation. |
| Paratyphoid | A similar condition to typhoid, caused by Salmonella enterica serotypes Paratyphi A, B, and C. | Generally milder than typhoid fever but has similar symptoms like fever, malaise, and gastrointestinal issues. |
Typhoid and paratyphoid fever, significant public health concerns, are systemic infections primarily caused by specific strains of the Salmonella bacteria. These illnesses present a unique challenge in terms of their spread and containment, especially in parts of the world grappling with inadequate sanitation infrastructure.
The primary cause...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.